|
|
Language/XML 2013. 7. 3. 11:18
4장 XML 스키마(Schema) 요점 및 보강 자료 1. 스키마란 - XML 문서의 구조와 엘리먼트, 속성들의 관계를 정의하여 다양한 자료형을 사용할 수 있도록 정의된 문서 구조
2. 스키마 구조의 장점 - xml 문법을 따른다.
- 풍부한 데이터형을 제공한다.
- 데이터의 제약 조건을 세밀하게 정의한다.
3. DTD 구조와 스키마 구조의 간단한 차이점 DTD | 스키마 | XML 1.0에서 제정 | XML 2.0에서 제정 | 익스플로러 4.0부터 도입 | 익스플로러 5.0부터 도입 | 확장자 DTD | 확장자 XSD | 데이터타입을 지원하는 기능이 부족 | 풍부한 데이터 타입을 지원 | 엘리먼트, 속성 등의 지원 기능이 미흡 | 엘리먼트, 속성 등의 지원 기능이 가능 | 데이터의 정렬이 어려움 | 데이터의 정렬이 가능 |
4. XSD 문서의 기본 형식 5. 이름 공간(namespace) 6. XSD와 XML 문서 연결하기 7. 엘리먼트 정의 - <complexType> 태그
- 하위 엘리먼트를 포함하거나 속성이 있는 엘리먼트를 선언 (복잡한 구조)
- <simpleType>태그
- 속성이나 하위 엘리먼트를 포함하지 않는 엘리먼트 (간단한 구조)
- <sequence> 태그
<도서목록> <도서> <분류>컴퓨터</분류> <제목>XML</제목> <출판사>정보</출판사> <저자>박준서, 최배근</저자> </도서> </도서목록> | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <!DOCTYPE 도서목록[ <!ELEMENT 도서목록 (도서) > <!ELEMENT 도서 (분류,제목,출판사,저자) > <!ELEMENT 분류 (#PCDATA) > <!ELEMENT 제목 (#PCDATA) > <!ELEMENT 출판사 (#PCDATA) <!ELEMENT 저자 (#PCDATA) > ]> |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <도서목록 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="도서목록04.xsd"> <도서> <분류>컴퓨터</분류> <제목>XML</제목> <출판사>정보</출판사> <저자>박준서, 최배근</저자> </도서> </도서목록> |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="도서목록"> <xsd:complexType> ☞ 도서목록 엘리먼트는 하위 엘리먼트를 포함 <xsd:sequence> ☞ 자식 엘리먼트들이 정의한 순서대로 반드시 정의 도서엘리먼트와 하위 엘리먼트는 생략 불가능 <xsd:element name="도서"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="분류" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="제목" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="출판사" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="저자" type="xsd:string" /> ☞ 분류,제목,출판사,저자태그는 문자형 생략 불가능
</xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:schema> |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="euc-kr" ?> <members> <member> <name>홍길동</name> <phone_no>031-111-2323</phone_no> </member> <member> <name>김유신</name> <phone_no>02-111-1234</phone_no> </member> </members> |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="euc-kr" ?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="members"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="member" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="name" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="phone_no" type="xsd:string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="2"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:schema> |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="euc-kr" ?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <!-- 루트요소 선언 --> <xsd:element name="members"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="member" type="memberType" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded" /> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> <!-- memberType 선언 --> <xsd:complexType name="memberType"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="name" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="phone_no" type="xsd:string" /> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema> |
- <minOccurs> 태그
- 엘리먼트의 최소 반복 횟수를 정의
- 생략시 기본값 = 1
- 0으로 정의시 : 엘리먼트는 생략
- 1로 정의시 : 반드시 엘리먼트 1번 정의
- <maxOccurs> 태그
- 엘리먼트의 최대 반복 횟수를 정의
- 생략시 기본값 = 1
- 1로 정의시 : 무조건 한번만 정의
- unbound로 정의시 반복 횟수에 제한 받지 않고 사용
- 도서목록14.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <도서목록 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="도서목록13.xsd"> <도서> <분류>컴퓨터</분류> <제목>XML</제목> <출판사>정보</출판사> <저자>박준서</저자> <저자>최배근</저자> </도서> <도서> <분류>컴퓨터</분류> <저자>박준서</저자> </도서> </도서목록> |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <element name="도서목록"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="도서" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="분류" type="string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" /> <element name="제목" type="string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" /> ☞ 제목 엘리먼트를 정의하지 않거나 한번 정의 (?) <element name="출판사" type="string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" /> ☞ 출판사 엘리먼트를 정의하지 않거나 여러번 정의 (*) <element name="저자" type="string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="2" /> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </schema> |
- <choice> 태그
- dtd에서의 |기호와 같은 역할
- 여러 가지 엘리먼트 중에서 한 개만을 정의
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <!DOCTYPE 도서목록[ ]> |
- 도서목록10.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <도서목록 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="도서목록09.xsd"> <도서> <제목>XML</제목> </도서> </도서목록> |
- 도서목록09.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <element name="도서목록"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="도서"> <complexType> <choice> ☞ 분류,제목,출판사,저자 엘리먼트 중에서 한 개를 선택해서 정의
<element name="분류" type="string" /> <element name="제목" type="string" /> <element name="출판사" type="string" /> <element name="저자" type="string" /> </choice> </complexType> </element> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </schema> |
- member2.xml : <member>의 자식 요소로 <name>과 <phone_no> 두 개의 요소를 가지거나
<lname>, <fname>, <phone_no> 세 개의 요소를 가질 수 있는 예 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <members> <member> <name>홍길동</name> <phone_no>031-111-2323</phone_no> </member> <member> <lname>김</lname> <fname>유신</fname> <phone_no>031-111-2323</phone_no> </member> </members> |
- member2.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="euc-kr" ?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <!-- 루트요소 선언 --> <xsd:element name="members"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="member" type="memberType" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded" /> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> <!-- memberType 선언 --> <xsd:complexType name="memberType"> <xsd:choice> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="name" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="phone_no" type="xsd:string" /> </xsd:sequence> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="lname" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="fname" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="phone_no" type="xsd:string" /> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:choice> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema> |
- <all> 태그
- 엘리먼트의 순서를 생각하지 않을 때 사용
- all 태그를 사용할 경우 복잡성을 줄이기 위한 제약사항
- 내부의 요소들은 반복이 1회까지로 제한
- choice 태그 안에서 사용할 수 없는 등 다른 복합자와 함께 사용될 때 제약이 존재
- 도서목록12.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <도서목록 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="도서목록11.xsd"> <도서> <제목>XML</제목> <분류>컴퓨터</분류> <저자>박준서</저자> <출판사>정보</출판사> </도서> </도서목록> |
- 도서목록11.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <element name="도서목록"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="도서"> <complexType> <all> ☞ 분류,제목,출판사,저자 엘리먼트는 순서를 생각하지 않는다.
<element name="분류" type="string" /> <element name="제목" type="string" /> <element name="출판사" type="string" /> <element name="저자" type="string" /> </all> </complexType> </element> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </schema> |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <members> <member> <name>홍길동</name> <phone_no>031-111-2323</phone_no> </member> </members> |
- member2-1.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="euc-kr" ?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <!-- 루트요소 선언 --> <xsd:element name="members"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="member" type="memberType" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded" /> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> <!-- memberType 선언 --> <xsd:complexType name="memberType"> <xsd:all> <xsd:element name="name" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="phone_no" type="xsd:string" /> </xsd:all> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:schema> |
- <default> 태그
- 엘리먼트의 값이 정의되지 않으면 default로 정의된 값을 할당
- <fixed> 태그
- 엘리먼트에 정의되는 값이 생략 또는
- fixed로 정의된 값이 엘리먼트의 값으로 정의
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <도서목록 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="도서목록15.xsd"> <도서> <분류></분류> <제목>XML</제목> </도서> </도서목록> |
- 도서목록15.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <element name="도서목록"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="도서" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="분류" type="string" default="컴퓨터" /> <element name="제목" type="string" fixed="XML" /> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </schema> |
- <group> 태그
- 엘리먼트의 반복을 쉽게 정의
- 반복되는 엘리먼트의 그룹을 <group>태그로 묶은 후 XSD에서 필요할 때 가져와서 사용
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <도서목록 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="도서목록17.xsd"> <도서> <분류>컴퓨터</분류> <제목>XML</제목> <출판사>정보</출판사> <저자>박준서</저자> </도서> </도서목록> |
- 도서목록17.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR" ?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:group name="myItem"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="분류" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="제목" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="출판사" type="xsd:string" /> <xsd:element name="저자" type="xsd:string" /> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:group>
<xsd:element name="도서목록"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="도서"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:group ref="myItem" /> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element>
</xsd:schema> |
8. 어트리뷰트 정의 - <simpleType>태그
- <enumeration>태그
- 여러 개의 정의된 값 중에서 하나의 속성만을 선택
- <length>태그
- <minLength>태그
- 어트리뷰트 데이터에 있는 문자의 최소 개수를 정의
- <maxLength>태그
- 어트리뷰터 데이터에 있는 문자의 최대 개수를 정의
- <minInclusive>태그
- <maxInclusive>태그
분류 속성은 "컴퓨터","소설","만화"라는 값중에 하나의 값만 가짐 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <도서목록 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="도서목록27.xsd"> <도서 분류="컴퓨터" 제목="XML" /> <도서 분류="소설" 제목="비와그리움" /> </도서목록> |
- 도서목록27.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <element name="도서목록"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="도서" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <complexType> <attribute name="분류"> <simpleType> <restriction base="string"> <enumeration value="컴퓨터" /> <enumeration value="소설" /> <enumeration value="만화" /> </restriction> </simpleType> </attribute> <attribute name="제목" type="string" /> </complexType> </element> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </schema> |
분류 속성 값의 길이는 3개, 제목 속성 값의 길이는 최소 1개 최대 6개이다. <?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <도서목록 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="도서목록29.xsd"> <도서 분류="컴퓨터" 제목="XML" /> <도서 분류="소설1" 제목="비와그리움" /> </도서목록> |
- 도서목록29.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <element name="도서목록"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="도서" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <complexType> <attribute name="분류"> <simpleType> <restriction base="string"> <length value="3" /> </restriction> </simpleType> </attribute> <attribute name="제목"> <simpleType> <restriction base="string"> <minLength value="1" /> <maxLength value="6" /> </restriction> </simpleType> </attribute> </complexType> </element> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </schema> |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <도서목록 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="도서목록31.xsd"> <도서 수량="10" /> </도서목록> |
- 도서목록31.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <element name="도서목록"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="도서" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <complexType> <attribute name="수량"> <simpleType> <restriction base="integer"> <minInclusive value="0" /> <maxInclusive value="10" /> </restriction> </simpleType> </attribute> </complexType> </element> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </schema> |
- 도서목록34.xml : 도서의 자식태그인 분류 태그는 컴퓨터, 소설, 만화라는 값중에 하나의 값만 가진다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <도서목록 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="도서목록33.xsd"> <도서> <분류>컴퓨터</분류> </도서> <도서> <분류>소설</분류> </도서> </도서목록> |
- 도서목록33.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="EUC-KR"?> <schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <element name="도서목록"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="도서" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <complexType> <sequence> <element name="분류"> <simpleType> <restriction base="string"> <enumeration value="컴퓨터" /> <enumeration value="소설" /> <enumeration value="만화" /> </restriction> </simpleType> </element> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </sequence> </complexType> </element> </schema> |
|
출처 - http://linuxism.tistory.com/911
Language/JAVASCRIPT 2013. 5. 22. 13:19
function setCaretPosition(ctrl, pos)
{
if(ctrl.setSelectionRange)
{
ctrl.focus();
ctrl.setSelectionRange(pos,pos);
}
else if (ctrl.createTextRange)
{
var range = ctrl.createTextRange();
range.collapse(true);
range.moveEnd('character', pos);
range.moveStart('character', pos);
range.select();
}
}
Language/JAVASCRIPT 2013. 4. 29. 19:40
http://msdn.microsoft.com/ko-kr/library/ie/hh673569%28v=vs.85%29.aspx#Enhanced_Event_Support
.NET Framework 3.0
Internet Explorer 10 및 JavaScript를 사용하는 Windows 스토어 앱은 새로운 표준에 대한 지원을 확장하고 일반적인 개발자 시나리오를 손쉽게 지원할 수 있도록 XMLHttpRequest 개체의 몇 가지 고급 기능을 제공합니다. 여기에는 다음과 같은 기능이 포함됩니다. - 플러그 인을 사용하지 않고 이미지, 동영상 및 오디오와 같은 이진 파일을 다운로드 및 업로드합니다.
- 플러그 인을 사용하지 않고 멀티미디어 콘텐츠 스트리밍을 다운로드합니다.
- XMLHttpRequest 작업 상태를 더 잘 관찰합니다.
- 다른 브라우저와의 상호 운용성을 개선합니다.
이러한 변경 내용은 다음 섹션에서 자세히 설명합니다.
이진 개체 업로드 및 다운로드
Internet Explorer 10에서는 XMLHttpRequest를 확장하여 이진 데이터를 지원합니다. 부분적으로 이 작업을 위해 파일 API 사양의 BLOB 인터페이스 지원을 추가합니다.
XMLHttpRequest 개체의 responseType 속성을 "blob"로 설정하면 요청과 관련된 데이터가 이진 데이터로 처리됩니다. 이 경우 다운로드 요청(예: GET)의 응답 속성 값에 영향을 줍니다.
다음 예제는 XMLHttpRequest를 사용하여 이미지를 BLOB 개체로 다운로드한 다음 그 결과를 웹 페이지의 이미지 요소에 할당하는 방법을 보여 줍니다.
var req = new XMLHttpReqest();
xhr.open("GET", "download?name=" + name, true);
xhr.responseType = "blob";
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState == xhr.DONE) {
var blob = xhr.reponse;
var image = document.getElementById("my-image");
image.addEventListener("load", function (evt) {
URL.revokeObjectURL(evt.target.src);
}
image.src = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
}
}
xhr.send();
다운로드 요청에 대해 responseType 속성을 "ms-stream"으로 설정하면 다음 예제와 같이 콘텐츠를 즉석에서 처리할 수 있습니다.
var req = new XMLHttpReqest();
xhr.open("GET", "download?name=" + name, true);
xhr.responseType = "ms-stream";
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState == xhr.LOADING) {
var stream = xhr.reponse;
var video = document.getElementById("my-video");
video.addEventListener("loadeddata", function (evt) {
URL.revokeObjectURL(evt.target.src);
}
video.src = URL.createObjectURL(stream);
}
}
xhr.send();
Comet 스트리밍 지원
Internet Explorer 10에서는 다음 예제와 같이 XMLHttpRequest 요청에 대한 응답을 로드하는 동안 responseText 속성을 읽을 수 있도록 하여 multipart HTTP 스트리밍(Comet 스트리밍이라고도 함)을 지원합니다.
xhr.open("GET", url);
xhr.timeout = timeout;
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState >= 3 && this.status == 200) {
var content = this.responseText;
handleContent(content);
}
}
xhr.send();
이전 Windows Internet Explorer 버전에서는 readyState 속성이 done으로 설정된 경우에만 responseText 속성을 읽을 수 있습니다.
responseText 속성은 현재까지 읽은 응답의 전체 값을 반환합니다. 응답이 수신될 때 개별 응답 패킷을 처리하려면 다음 예제와 같이 progress 이벤트(다음 섹션에 설명됨)를 사용하거나 각 readyStateChange 이벤트 반복의 responseText 길이를 추적할 수 있습니다.
xhr.open("GET", url);
xhr.timeout = timeout;
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (typeof this.index == "undefined")
this.index = 0;
if (this.readyState >= 3 && this.status == 200) {
var content = this.responseText;
handleContent( content.substring(this.index) )
this.index = content.length;
}
}
xhr.send();
고급 이벤트 지원
Internet Explorer 10에서는 XMLHttpRequest 개체를 확장하여 XMLHttpRequest 수준 2 사양에 지정된 다음 이벤트를 지원합니다.
| 이벤트 | 설명 |
|---|
|
loadstart
|
요청이 시작될 때 발생합니다.
|
|
progress
|
요청이 데이터를 보내거나 받는 동안 서버에서 정의된 간격으로 발생합니다.
|
|
abort
|
요청이 취소될 때(예: abort() 메서드가 호출될 때) 발생합니다.
|
|
error
|
요청이 실패할 때 발생합니다.
|
|
load
|
요청이 성공적으로 완료될 때 발생합니다.
|
|
timeout
|
작성자가 지정한 기간이 경과할 때 발생합니다.
|
|
loadend
|
성공 여부에 관계없이 요청이 완료될 때 발생합니다.
|
XMLHttpRequest 개체의 이벤트 처리는 다음 예제와 같이 DOM 이벤트 수준 3 사양 및 진행률 이벤트 사양에 지정된 모델을 따릅니다.
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
var url = "some-url";
xhr.timeout = 5000;
xhr.addEventListener("timeout", handleTimeout(evt), false);
xhr.onprogress = function(evt) {
handleEvent("data: " + this.responseText);
// Calculate progress
var str = "";
if (evt.lengthComputable) {
var percent = 100 * evt.loaded / evt.total;
str = percent + "%. Current total size: " + this.responseText.length);
} else {
str = "Progress unknown. Current total size: " + this.responseText.length;
}
updateProgress(str);
}
xhr.open("GET", url);
xhr.send();
XMLHttpRequest에 대한 CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)
Internet Explorer 10에서는 XMLHttpRequest(XHR) 개체와 관련하여 CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)를 새롭게 지원합니다. CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) 사양에 정의된 CORS는 HTTP 헤더를 사용하여 대개 동일한 사이트 출처 정책으로 제한되는 도메인 간 웹 요청을 가능하게 합니다.
기본적으로 동일한 사이트 출처 정책은 웹 사이트가 다른 도메인에 있는 서버의 리소스를 요청하지 못하도록 합니다. 그러나
XMLHttpRequest(XHR) 요청에 대한 CORS를 지원하는 브라우저는 적절한 관리자가 해당 요청을 허용하도록 선택할 경우
다른 도메인의 리소스에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
웹 페이지가 XHR request를 수행하면 Internet Explorer에서 원본 헤더를 대상 서버로 보냅니다. 헤더에는
요청의 프로토콜 체계(http:// 또는 https://) 및 요청하는 웹 페이지의 호스트 이름이 포함됩니다. 대상 서버는
요청을 승인할 경우 Access-Control-Allow-Origin 헤더를 반환하며 요청을 처리할 수 있습니다.
이제 XMLHttpRequest 개체가 XHR 요청에 권한 부여 메커니즘을 포함할 수 있게 하는 withCredentials 속성을 지원합니다. 자세한 내용은 XMLHttpRequest 수준 2 사양을 참조하세요.
다음 예제와 같이 withCredentials 속성을 사용하여 CORS 지원을 검색할 수 있습니다.
var url = "http://contoso.com/services/"
if( window.XMLHttpRequest ) {
var oReq = new XMLHttpRequest();
if( oReq.withCredentials == undefined ) {
oReq.open("GET", url, true);
oReq.onload = handleResponse();
oReq.send( null );
} else {
// CORS not support. Handle fallback
}
} else {
// XMLHttpRequest not supported; handle fallback
}
CORS의 실습 데모는 IE 테스트 드라이브의 실습: 사이트 간 업로드(영문)를 참조하세요.
관련 항목
-
DOM(문서 개체 모델)
-
개발자용 Internet Explorer 10 가이드
Language/JAVASCRIPT 2013. 4. 29. 18:09
http://www.w3.org/TR/XMLHttpRequest2/#event-xhr-load

XMLHttpRequest Level 2
W3C Working Draft 17 January 2012
- This Version:
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2012/WD-XMLHttpRequest-20120117/
- Latest Version:
- http://www.w3.org/TR/XMLHttpRequest/
- Latest Editor Draft:
- http://dvcs.w3.org/hg/xhr/raw-file/tip/Overview.html
- Previous Versions:
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2011/WD-XMLHttpRequest2-20110816/
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2010/WD-XMLHttpRequest2-20100907/
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2009/WD-XMLHttpRequest2-20090820/
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2008/WD-XMLHttpRequest2-20080930/
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2008/WD-XMLHttpRequest2-20080225/
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2007/WD-XMLHttpRequest-20071026/
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2007/WD-XMLHttpRequest-20070618/
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2007/WD-XMLHttpRequest-20070227/
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2006/WD-XMLHttpRequest-20060927/
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2006/WD-XMLHttpRequest-20060619/
- http://www.w3.org/TR/2006/WD-XMLHttpRequest-20060405/
- Editor:
- Anne van Kesteren
(Opera Software ASA)
<annevk@opera.com>
Abstract
The XMLHttpRequest specification defines an API that provides scripted
client functionality for transferring data between a client and a server.
Status of this Document
This section describes the status of this document at the time of its
publication. Other documents may supersede this document. A list of current
W3C publications and the latest revision of this technical report can be
found in the W3C technical reports index
at http://www.w3.org/TR/.
This is the 17 January 2012 W3C Working Draft of XMLHttpRequest Level 2.
Please send comments to
public-webapps@w3.org
(archived)
with [XHR] at the start of the subject line.
This document is produced by the
Web Applications (WebApps) Working Group.
The WebApps Working Group is part of the
Rich Web Clients Activity
in the W3C Interaction Domain.
This document was produced by a group operating under the
5 February 2004
W3C Patent Policy. W3C maintains a
public
list of any patent disclosures made in connection with the deliverables of
the group; that page also includes instructions for disclosing a patent. An
individual who has actual knowledge of a patent which the individual believes
contains
Essential
Claim(s) must disclose the information in accordance with
section
6 of the W3C Patent Policy.
Publication as a Working Draft does not imply endorsement by the W3C
Membership. This is a draft document and may be updated, replaced or
obsoleted by other documents at any time. It is inappropriate to cite this
document as other than work in progress.
This document supersedes
XMLHttpRequest 1.
Table of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 1.1 Specification history
- 2 Conformance
- 2.1 Dependencies
- 2.2 Extensibility
- 3 Terminology
- 4 Interface
XMLHttpRequest
- 4.1 Origin and base URL
- 4.2 Task sources
- 4.3 Constructors
- 4.4 Garbage collection
- 4.5 Event handlers
- 4.6 States
- 4.7 Request
- 4.7.1 The
open() method - 4.7.2 The
setRequestHeader() method - 4.7.3 The
timeout attribute - 4.7.4 The
withCredentials attribute - 4.7.5 The
upload attribute - 4.7.6 The
send() method - 4.7.7 Infrastructure for the
send() method - 4.7.8 The
abort() method
- 4.8 Response
- 4.8.1 The
status attribute - 4.8.2 The
statusText attribute - 4.8.3 The
getResponseHeader() method - 4.8.4 The
getAllResponseHeaders() method - 4.8.5 Response entity body
- 4.8.6 The
overrideMimeType() method - 4.8.7 The
responseType attribute - 4.8.8 The
response attribute - 4.8.9 The
responseText attribute - 4.8.10 The
responseXML attribute
- 4.9 Events summary
- 5 Interface
FormData
- 5.1 Constructors
- 5.2 The
append() method
- References
- Normative references
- Acknowledgments
1 Introduction
This section is non-normative.
The XMLHttpRequest object is the ECMAScript HTTP API.
[ECMASCRIPT]
The name of the object is XMLHttpRequest for compatibility
with the Web, though each component of this name is potentially
misleading. First, the object supports any text based format, including
XML. Second, it can be used to make requests over both HTTP and HTTPS
(some implementations support protocols in addition to HTTP and HTTPS, but
that functionality is not covered by this specification). Finally, it
supports "requests" in a broad sense of the term as it pertains to HTTP;
namely all activity involved with HTTP requests or responses for the
defined HTTP methods.
Some simple code to do something with data from an XML document
fetched over the network:
function processData(data) {
// taking care of data
}
function handler() {
if(this.readyState == this.DONE) {
if(this.status == 200 &&
this.responseXML != null &&
this.responseXML.getElementById('test').textContent) {
// success!
processData(this.responseXML.getElementById('test').textContent);
return;
}
// something went wrong
processData(null);
}
}
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.onreadystatechange = handler;
client.open("GET", "unicorn.xml");
client.send();
If you just want to log a message to the server:
function log(message) {
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.open("POST", "/log");
client.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=UTF-8");
client.send(message);
}
Or if you want to check the status of a document on the server:
function fetchStatus(address) {
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.onreadystatechange = function() {
// in case of network errors this might not give reliable results
if(this.readyState == this.DONE)
returnStatus(this.status);
}
client.open("HEAD", address);
client.send();
}
1.1 Specification history
The XMLHttpRequest object was initially defined as part of
the WHATWG's HTML effort. (Long after Microsoft shipped an implementation.)
It moved to the W3C in 2006. Extensions (e.g. progress events and
cross-origin requests) to XMLHttpRequest were developed in a
separate draft (XMLHttpRequest Level 2) until end of 2011, at which point
the two drafts were merged and XMLHttpRequest became a single
entity again from a standards perspective.
Historical discussion can be found in the following mailing list
archives:
All diagrams, examples, and notes in this specification are
non-normative, as are all sections explicitly marked non-normative.
Everything else in this specification is normative.
The key words "MUST", "MUST NOT", "REQUIRED", "SHOULD", "SHOULD NOT", "RECOMMENDED", "MAY", and
"OPTIONAL" in the normative parts of this specification are to be
interpreted as described in RFC2119. For readability, these words do
not appear in all uppercase letters in this specification.
[RFC2119]
2.1 Dependencies
This specification relies on several underlying specifications.
- Cross-Origin Resource Sharing
A conforming user agent must
support the algorithms of the Cross-Origin Resource Sharing
specification. [CORS] - DOM4
A conforming user agent must
support at least the subset of the functionality defined in DOM4 that
this specification relies upon, such as various exceptions and
EventTarget. [DOM] - File API
A conforming user agent must
support at least the subset of the functionality defined in File API that
this specification relies upon, such as the Blob and
File interfaces. [FILEAPI]
- HTML
A conforming user agent must
support at least the subset of the functionality defined in HTML that
this specification relies upon, such as the basics of the
Window object and serializing a Document
object. [HTML]
- HTTP
A conforming user agent must
support some version of the HTTP protocol. Requirements regarding HTTP
are made throughout the specification. [HTTP]
- Progress Events
A conforming user agent must support the
Progress Events specification.
[PROGRESSEVENTS]
- Typed Array
A conforming user agent must support the
ArrayBuffer object.
[TYPEDARRAY]
- Web IDL
A conforming user agent must also
be a conforming implementation of the IDL fragments in this
specification, as described in the Web IDL specification.
[WEBIDL]
- XML
A conforming user agent must be a
conforming XML processor that reports violations of namespace
well-formedness. [XML]
[XMLNS]
2.2 Extensibility
User agents, Working Groups, and other interested parties are
strongly encouraged to discuss new features on a relevant public
forum, preferably
public-webapps@w3.org. If this
is for some reason not possible prefix the extension in some way. E.g. if
company Foo wants to add a proprietary method bar() it could
be named fooBar() to prevent clashes with a potential
non-proprietary method bar().
3 Terminology
The term user credentials for the purposes of this
specification means cookies, HTTP authentication, and client-side SSL
certificates. Specifically it does not refer to proxy authentication or
the Origin header.
[COOKIES]
To deflate a DOMString into a byte sequence means to create
a sequence of bytes such that the nth byte of the
sequence is equal to the low-order byte of the nth
code point in the original DOMString.
To inflate a byte sequence into a DOMString means to create
a DOMString such that the nth code point has 0x00 as
the high-order byte and the nth byte of the byte
sequence as the low-order byte.
4 Interface XMLHttpRequest
[NoInterfaceObject]
interface XMLHttpRequestEventTarget : EventTarget {
// event handlers
[TreatNonCallableAsNull] attribute Function? onloadstart;
[TreatNonCallableAsNull] attribute Function? onprogress;
[TreatNonCallableAsNull] attribute Function? onabort;
[TreatNonCallableAsNull] attribute Function? onerror;
[TreatNonCallableAsNull] attribute Function? onload;
[TreatNonCallableAsNull] attribute Function? ontimeout;
[TreatNonCallableAsNull] attribute Function? onloadend;
};
interface XMLHttpRequestUpload : XMLHttpRequestEventTarget {
};
enum XMLHttpRequestResponseType {
"",
"arraybuffer",
"blob",
"document",
"json",
"text"
}
[Constructor]
interface XMLHttpRequest : XMLHttpRequestEventTarget {
// event handler
[TreatNonCallableAsNull] attribute Function? onreadystatechange;
// states
const unsigned short UNSENT = 0;
const unsigned short OPENED = 1;
const unsigned short HEADERS_RECEIVED = 2;
const unsigned short LOADING = 3;
const unsigned short DONE = 4;
readonly attribute unsigned short readyState;
// request
void open(DOMString method, DOMString url, optional boolean async, optional DOMString? user, optional DOMString? password);
void setRequestHeader(DOMString header, DOMString value);
attribute unsigned long timeout;
attribute boolean withCredentials;
readonly attribute XMLHttpRequestUpload upload;
void send();
void send(ArrayBuffer data);
void send(Blob data);
void send(Document data);
void send(DOMString? data);
void send(FormData data);
void abort();
// response
readonly attribute unsigned short status;
readonly attribute DOMString statusText;
DOMString getResponseHeader(DOMString header);
DOMString getAllResponseHeaders();
void overrideMimeType(DOMString mime);
attribute XMLHttpRequestResponseType responseType;
readonly attribute any response;
readonly attribute DOMString responseText;
readonly attribute Document responseXML;
};
[Constructor]
interface AnonXMLHttpRequest : XMLHttpRequest {
};
4.1 Origin and base URL
Each XMLHttpRequest object has an associated
XMLHttpRequest origin and an
XMLHttpRequest base URL.
This specification defines their values when the global object is
represented by the Window object. When
the XMLHttpRequest object is used in other contexts their
values will have to be defined as appropriate for that context. That is
considered to be out of scope for this specification.
In environments where the global object is represented by the
Window object the
XMLHttpRequest object has an associated
XMLHttpRequest document which is the
document
associated with the Window object for
which the XMLHttpRequest interface object was created.
The
XMLHttpRequest document is used to
determine the XMLHttpRequest origin and
XMLHttpRequest base URL at a later stage.
4.2 Task sources
Each XMLHttpRequest object has its own
task source. Namely, the
XMLHttpRequest task source.
4.3 Constructors
The XMLHttpRequest object has an associated
anonymous flag. If the anonymous flag is set,
user credentials and the
XMLHttpRequest origin are not exposed when
fetching resources. It can
only be set to true by using the
AnonXMLHttpRequest()
constructor.
- client = new
XMLHttpRequest() - Returns a new
XMLHttpRequest object. - client = new
AnonXMLHttpRequest() - Returns a new
AnonXMLHttpRequest object that has the
anonymous flag set.
The XMLHttpRequest()
constructor must return a new XMLHttpRequest object.
The
AnonXMLHttpRequest()
constructor must return a new AnonXMLHttpRequest object with
its anonymous flag set.
4.4 Garbage collection
An XMLHttpRequest object must not be garbage collected if
its state is OPENED and the
send() flag is set, its state is
HEADERS_RECEIVED, or
its state is LOADING, and
one of the following is true:
It has one or more
event listeners
registered whose type is
readystatechange,
progress,
abort,
error,
load,
timeout, or
loadend.
The upload complete flag is unset and the associated
XMLHttpRequestUpload object has one or more
event listeners
registered whose type is
progress,
abort,
error,
load,
timeout, or
loadend.
If an XMLHttpRequest object is garbage collected while its
connection is still open, the user agent must cancel any instance of the
fetch algorithm opened by this object,
discarding any tasks
queued for them, and
discarding any further data received from the network for them.
4.5 Event handlers
The following are the
event handlers (and their corresponding
event handler event types)
that must be supported on objects implementing an interface that inherits
from XMLHttpRequestEventTarget as attributes:
The following is the
event handler
(and its corresponding
event handler event type) that must be
supported as attribute solely by the
XMLHttpRequest object:
4.6 States
- client .
readyState Returns the current state.
The XMLHttpRequest object can be in several states. The
readyState
attribute must return the current state, which must be one of the
following values:
UNSENT
(numeric value 0)The object has been constructed. OPENED
(numeric value 1)The open() method has been successfully invoked.
During this state request headers can be set using
setRequestHeader()
and the request can be made using the
send() method. -
(numeric value 2)
All redirects (if any) have been followed and all HTTP headers of
the final response have been received. Several response members of the
object are now available. LOADING
(numeric value 3)The response entity body is being received. DONE
(numeric value 4)The data transfer has been completed or something went wrong
during the transfer (e.g. infinite redirects).
The send() flag indicates
that the send() method has
been invoked. It is initially unset and is used during the
OPENED state.
The error flag indicates some type of
network error or request abortion. It is initially unset and is used
during the DONE state.
4.7 Request
The XMLHttpRequest object holds the following request
metadata variables:
- synchronous flag
- Set when fetching is
done synchronously. Initially unset.
- request method
- The HTTP method used in the request.
- request URL
- The resolved URL used in the
request.
- request username
- The username used in the request or null if there is no
username.
- request password
- The password used in the request or null if there is no
password.
- A list consisting of HTTP header name/value pairs to be used in the
request.
- request entity body
- The entity body used in the
request or null if there is no
entity body.
- upload complete flag
- Set when no more events are to be dispatched on the
XMLHttpRequestUpload object. Initially unset.
- upload events flag
- Set when event listeners are registered on the
XMLHttpRequestUpload object to determine whether a preflight
request is needed. Initially unset.
The XMLHttpRequest object also has an associated
XMLHttpRequestUpload object.
4.7.1 The open() method
- client .
open(method,
url, async, user,
password) -
Sets the request method, request URL,
synchronous flag, request username, and
request password.
Throws a "SyntaxError" exception if
one of the following is true:
- method is not a valid HTTP method.
- url cannot be resolved.
- url contains the
"user:password"
format in the userinfo production.
Throws a "SecurityError" exception
if method is a case-insensitive match for
CONNECT, TRACE or TRACK.
Throws an "InvalidAccessError"
exception if one of the following is true:
The
open(method, url, async, user, password)
method must run these steps (unless otherwise indicated):
-
If there is an associated
XMLHttpRequest document run
these substeps:
If the
XMLHttpRequest document is not
fully active,
throw an
"InvalidStateError" exception and
terminate the overall set of steps.
Let XMLHttpRequest base URL be the
document base URL of the
XMLHttpRequest document. Let XMLHttpRequest origin be the
origin of the
XMLHttpRequest document
and let it be a globally unique identifier if the
anonymous flag is set.
If any code point in method is higher than
U+00FF LATIN SMALL LETTER Y WITH DIAERESIS or after
deflating
method it does not match the
Method token production,
throw a
"SyntaxError" exception and terminate
these steps. Otherwise let method be the result of
deflating
method. -
If method is a case-insensitive match for
CONNECT, DELETE, GET,
HEAD, OPTIONS, POST,
PUT, TRACE, or TRACK
subtract 0x20 from each byte in the range 0x61 (ASCII a) to
0x7A (ASCII z).
If it does not match any of the above, it is passed
through literally, including in the final request.
-
If method is a case-sensitive match for
CONNECT, TRACE, or TRACK,
throw a
"SecurityError" exception and
terminate these steps.
Allowing these methods poses a security risk.
[HTTPVERBSEC]
Let url be a
URL with character encoding UTF-8.
Resolve url
relative to the XMLHttpRequest base URL.
If the algorithm returns an error,
throw a
"SyntaxError" exception and terminate
these steps.
Drop
<fragment> from
url. If the "user:password" format in the
userinfo production is not supported
for the relevant
<scheme> and
url contains this format,
throw a
"SyntaxError" and terminate these
steps.
If url contains the "user:password"
format let temp user be the user part and
temp password be the password part. If url just contains the "user"
format let temp user be the user part. -
Let async be the value of the async argument or
true if it was omitted.
If async is false, there is an associated
XMLHttpRequest document and either the
timeout attribute value is
not zero, the
withCredentials
attribute value is true, or the
responseType
attribute value is not the empty string,
throw an
"InvalidAccessError" exception and
terminate these steps.
-
If the user argument was not omitted follow these
sub steps:
If user is not null and the
origin of url is not
same origin with the
XMLHttpRequest origin,
throw an
"InvalidAccessError" exception and
terminate the overall set of steps.
Let temp user be user.
These steps override anything that may have been set by
the url argument.
-
If the password argument was not omitted follow
these sub steps:
If password is not null and the
origin of url is not
same origin with the
XMLHttpRequest origin,
throw an
"InvalidAccessError" exception and
terminate the overall set of steps. Let temp password be password.
These steps override anything that may have been set by
the url argument.
Terminate the abort() algorithm. Terminate the send() algorithm. The user agent should cancel any network
activity for which the object is responsible. If there are any
tasks from the
object's XMLHttpRequest task source in one of
the task queues,
then remove them.
-
Set variables associated with the object as follows:
Change the state to
OPENED. Fire an event named readystatechange.
- client .
setRequestHeader(header, value) -
Appends an header to the list of
author request headers, or if header is already
in the list of author request headers, combines its value
with value.
Throws an "InvalidStateError"
exception if the state is not
OPENED or if the
send() flag is set.
Throws a "SyntaxError" exception if
header is not a valid HTTP header field name or if
value is not a valid HTTP header field value.
As indicated in the algorithm below certain headers cannot
be set and are left up to the user agent. In addition there are certain
other headers the user agent will take control of if they are not set by
the author as indicated at the end of the
send() method section.
For non same origin requests using the HTTP
GET method a preflight request is made when headers other
than Accept and Accept-Language are set.
The
method must run these steps:
If the state is not
OPENED,
throw an
"InvalidStateError" exception and
terminate these steps.
If the send() flag is set,
throw an
"InvalidStateError" exception and
terminate these steps.
If any code point in header is higher than
U+00FF LATIN SMALL LETTER Y WITH DIAERESIS or after
deflating
header it does not match the
field-name production,
throw a
"SyntaxError" exception and terminate
these steps. Otherwise let header be the result of
deflating
header. -
If any code point in value is higher than
U+00FF LATIN SMALL LETTER Y WITH DIAERESIS or after
deflating
value it does not match the
field-value production,
throw a
"SyntaxError" exception and terminate
these steps. Otherwise let value be the result of
deflating
value.
The empty string is legal and represents the empty
header value.
-
Terminate these steps if header is a case-insensitive
match for one of the following headers:
Accept-CharsetAccept-EncodingAccess-Control-Request-HeadersAccess-Control-Request-MethodConnectionContent-LengthCookieCookie2Content-Transfer-EncodingDateExpectHostKeep-AliveOriginRefererTETrailerTransfer-EncodingUpgradeUser-AgentVia
… or if the start of header is a case-insensitive
match for Proxy- or Sec- (including when
header is just Proxy- or Sec-).
The above headers are controlled by the user agent to
let it control those aspects of transport. This guarantees data
integrity to some extent. Header names starting with Sec-
are not allowed to be set to allow new headers to be minted that are
guaranteed not to come from XMLHttpRequest.
If header is not in the
author request headers list append header with
its associated value to the list and terminate these
steps. If header is in the author request headers
list either use multiple headers, combine the values or use a combination
of those (section 4.2, RFC 2616).
[HTTP]
See also the
send() method regarding user
agent header handling for caching, authentication, proxies, and
cookies.
Some simple code demonstrating what happens when setting the same
header twice:
// The following script:
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.open('GET', 'demo.cgi');
client.setRequestHeader('X-Test', 'one');
client.setRequestHeader('X-Test', 'two');
client.send();
// …results in the following header being sent:
X-Test: one, two
4.7.3 The timeout attribute
- client .
timeout -
The amount of milliseconds a request can take before being
terminated. Initially zero. Zero means there is no timeout.
When set: throws an
"InvalidAccessError" exception if
the synchronous flag is set when there is an
associated XMLHttpRequest document.
The
timeout
attribute must return its value. Initially its value must be zero.
Setting the timeout
attribute must run these steps:
If there is an associated
XMLHttpRequest document and the
synchronous flag is set,
throw an
"InvalidAccessError" exception and
terminate these steps.
Set its value to the new value.
This implies that the
timeout attribute can be
set while fetching is in
progress. If that occurs it will still be measured relative to the start
of fetching.
4.7.4 The withCredentials attribute
- client .
withCredentials -
True when user credentials are to be included in a
cross-origin request. False when they are to be excluded in a
cross-origin request and when cookies are to be ignored in its response.
Initially false.
When set: throws an
"InvalidStateError" exception if the
state is not UNSENT or
OPENED, or if
the send() flag is set.
When set: throws an
"InvalidAccessError" exception if
either the synchronous flag is set when there is an
associated XMLHttpRequest document or if the
anonymous flag is set.
The
withCredentials
attribute must return its value. Initially its value must be false.
Setting the
withCredentials
attribute must run these steps:
If the state is not
UNSENT or
OPENED,
throw an
"InvalidStateError" exception and
terminate these steps.
If the send() flag is set,
throw an
"InvalidStateError" exception and
terminate these steps.
If the anonymous flag is set,
throw an
"InvalidAccessError" exception and
terminate these steps.
If there is an associated
XMLHttpRequest document and the
synchronous flag is set,
throw an
"InvalidAccessError" exception and
terminate these steps.
Set the
withCredentials
attribute's value to the given value.
The
withCredentials
attribute has no effect when
fetching
same-origin
resources.
4.7.5 The upload attribute
- client .
upload Returns the associated XMLHttpRequestUpload
object.
The
upload
attribute must return the associated
XMLHttpRequestUpload object.
4.7.6 The send() method
- client .
send(data) -
Initiates the request. The optional argument provides the
request entity body. The argument is ignored if
request method is GET or
HEAD.
Throws an "InvalidStateError"
exception if the state is not
OPENED or if the
send() flag is set.
The
send(data)
method must run these steps (unless otherwise noted). This algorithm can
be terminated by invoking the
open() or
abort() method. When it is
terminated the user agent
must terminate the algorithm after finishing the step it is on.
The send()
algorithm can only be terminated if the synchronous flag is
unset and only after the method call has returned.
If the state is not
OPENED,
throw an
"InvalidStateError" exception and
terminate these steps.
If the send() flag is set,
throw an
"InvalidStateError" exception and
terminate these steps.
-
If the request method is a case-sensitive match for
GET or HEAD act as if data
is null.
If the data argument has been omitted or is
null, do not include a request entity body
and go to the next step.
Otherwise, let encoding be null, mime type be
null, and then follow these rules:
- If data is a
ArrayBuffer Let the request entity body be the raw data
represented by data. - If data is a
Blob -
If the object's
type
attribute is not the empty string let mime type be its
value.
Let the request entity body be the raw data
represented by data.
- If data is a
Document
-
Let encoding be the
preferred MIME name of the
character encoding
of data. If encoding is UTF-16 change it to
UTF-8.
Let mime type be "application/xml" or
"text/html" if
Document is an
HTML document, followed by
";charset=", followed by encoding.
Let the request entity body be the result of getting
the innerHTML
attribute on data
converted to Unicode
and encoded as encoding. Re-throw any exception this
throws.
In particular, if the document cannot be serialized an
"InvalidStateError" exception is
thrown.
Subsequent changes to the
Document have no effect on what
is transferred.
- If data is a string
-
Let encoding be UTF-8.
Let mime type be "text/plain;charset=UTF-8".
Let the request entity body be data
converted to Unicode
and encoded as UTF-8.
- If data is a
FormData -
Let the request entity body be the result of running
the
multipart/form-data encoding algorithm
with data as form data set and with UTF-8 as the
explicit character encoding.
Let mime type be the concatenation of
"multipart/form-data;",
a U+0020 SPACE character,
"boundary=", and the
multipart/form-data boundary string
generated by the
multipart/form-data encoding algorithm.
If a Content-Type header is in
author request headers and its value is a
valid MIME type that has a
charset parameter whose value is not a case-insensitive
match for encoding, and encoding
is not null, set all the charset parameters of that
Content-Type header to encoding.
If no Content-Type header is in
author request headers and mime type is
not null, append a Content-Type header with value
mime type to author request headers.
If the synchronous flag is set, release the
storage mutex. If the synchronous flag is unset and one or more
event listeners are registered on the XMLHttpRequestUpload
object, set the upload events flag.
Unset the error flag. Set the upload complete flag if there is no
request entity body or if the
request entity body is empty.
-
If the synchronous flag is unset, run these substeps:
Set the send() flag.
-
Fire an event named readystatechange.
The state does not change. The event is dispatched for
historical reasons.
Fire a progress event named loadstart. If the upload complete flag is unset,
fire a progress event named loadstart
on the XMLHttpRequestUpload object. Return the send()
method call, but continue running the steps in this algorithm.
-
- If the
XMLHttpRequest origin and the
request URL are same origin -
These are the same-origin request steps.
Fetch the
request URL from origin
XMLHttpRequest origin, with the
synchronous flag set if the
synchronous flag is set, using HTTP method
request method, user request username (if
non-null) and password request password (if non-null),
taking into account the request entity body, list of
author request headers and the rules listed at the end of
this section.
- If the synchronous flag is set
-
While making the request also follow the
same-origin request event rules.
The
send() method call will
now be returned by virtue of this algorithm ending.
- If the synchronous flag is unset
-
Make upload progress notifications.
Make progress notifications.
While processing the request, as data becomes available and when
the user interferes with the request,
queue tasks
to update the response entity body and follow the
same-origin request event rules.
- Otherwise
-
These are the cross-origin request steps.
Make a cross-origin request,
passing these as parameters:
- request URL
- The request URL.
- request method
- The request method.
- author request headers
- The list of author request headers.
- request entity body
- The request entity body.
- source origin
- The
XMLHttpRequest origin. - credentials flag
- The
withCredentials
attribute's value. - force preflight flag
- True if the upload events flag is set, or false
otherwise.
Request username and
request password are always ignored as part of a
cross-origin request; including
them would allow a site to perform a distributed password search.
However, user agents will include user credentials in the
request (if the user has any and if
withCredentials
is true).
- If the synchronous flag is set
-
While making the request also follow the
cross-origin request event rules.
The
send() method call will
now be returned by virtue of this algorithm ending.
- If the synchronous flag is unset
-
While processing the request, as data becomes available and when
the end user interferes with the request,
queue tasks to update the
response entity body and follow the
cross-origin request event rules.
If the user agent allows the end user to configure a proxy it
should modify the request appropriately; i.e., connect
to the proxy host instead of the origin server, modify the
Request-Line and send Proxy-Authorization
headers as specified.
If the user agent supports HTTP Authentication and
Authorization is not in the list
of author request headers, it should
consider requests originating from the XMLHttpRequest object
to be part of the protection space that includes the accessed URIs and
send Authorization headers and
handle 401 Unauthorized requests appropriately.
If authentication fails,
XMLHttpRequest origin and the
request URL are same origin,
Authorization is not in the list
of author request headers, request username is
null, and request password is null, user agents
should prompt the end user for their username and
password.
Otherwise, if authentication fails, user agents
must not prompt the end user for their username and
password. [HTTPAUTH]
End users are not prompted for various cases so that
authors can implement their own user interface.
If the user agent supports HTTP State Management it
should persist, discard and send cookies (as received
in the Set-Cookie response header, and sent in the
Cookie header) as applicable.
[COOKIES]
If the user agent implements a HTTP cache it should
respect Cache-Control headers in
author request headers
(e.g. Cache-Control: no-cache bypasses the cache). It
must not send Cache-Control or
Pragma request headers automatically unless the end user
explicitly requests such behavior (e.g. by reloading the page).
For 304 Not Modified responses that are a result of a
user agent generated conditional request the user agent
must act as if the server gave a 200 OK
response with the appropriate content. The user agent
must allow author request headers to override automatic cache
validation (e.g. If-None-Match or
If-Modified-Since), in which case
304 Not Modified responses must be passed through.
[HTTP]
If the user agent implements server-driven content-negotiation
it must follow these constraints for the
Accept and Accept-Language request headers:
Responses must have the content-encodings
automatically decoded. [HTTP]
Besides the author request headers, user agents
should not include additional request headers other than those mentioned
above or other than those authors are not allowed to set using
setRequestHeader().
This ensures that authors have a predictable API.
4.7.7 Infrastructure for the send() method
The same-origin request event rules are as follows:
- If the response has an HTTP status code of 301, 302, 303, or 307
-
If the redirect violates infinite loop precautions this is a
network error.
Otherwise, run these steps:
Set the request URL to the
URL conveyed by the
Location header. If the XMLHttpRequest origin and the
origin of request URL
are same origin transparently follow
the redirect while observing the
same-origin request event rules.
Otherwise, follow the cross-origin request steps
and terminate the steps for this algorithm.
HTTP places requirements on the user agent regarding the
preservation of the request method and
request entity body during redirects, and also requires end
users to be notified of certain kinds of automatic redirections.
- If the end user cancels the request
This is an abort error. - If there is a network error
-
In case of DNS errors, TLS negotiation failure, or other type of
network errors, this is a network error. Do not request any
kind of end user interaction.
This does not include HTTP responses that indicate
some type of error, such as HTTP status code 410.
- If
timeout is not 0
and since the request started the amount of milliseconds specified by
timeout has passed This is a timeout error. - Once all HTTP headers have been received, the
synchronous flag is unset, and the HTTP status code of the
response is not 301, 302, 303, or 307
Switch to the HEADERS_RECEIVED state. - Once the first byte (or more) of the
response entity body has been received and the
synchronous flag is unset
- If there is no response entity body and the
synchronous flag is unset
Switch to the LOADING state. - Once the whole response entity body has been
received
- If there is no response entity body and the state is
LOADING
- If there is no response entity body and the
synchronous flag is set
Switch to the DONE state.
The cross-origin request event rules are as follows:
- If the cross-origin request status
is preflight complete and the synchronous flag is
unset
Make upload progress notifications. - If the cross-origin request status
is network error
This is a network error. - If the cross-origin request status
is abort error
This is an abort error. - If
timeout is not 0
and since the request started the amount of milliseconds specified by
timeout has passed This is a timeout error. - Once all HTTP headers have been received, the
cross-origin request status is
success, and the synchronous flag is unset
-
Switch to the HEADERS_RECEIVED state.
Make progress notifications.
- Once the first byte (or more) of the
response entity body has been received, the
cross-origin request status is
success, and the synchronous flag is unset
- If there is no response entity body, the
cross-origin request status is
success, and the synchronous flag is unset
Switch to the LOADING state. - Once the whole response entity body has been received
and the cross-origin request status is
success
- If there is no response entity body, the
cross-origin request status is
success, and the state is
LOADING
- If there is no response entity body, the
cross-origin request status is
success, and the synchronous flag is set
Switch to the DONE state.
When something is said to be a network error run the
request error steps for exception
"NetworkError" and
event error.
When something is said to be an abort error run the
request error steps for exception
"AbortError" and event
abort.
When something is said to be an timeout error run the
request error steps for exception
"TimeoutError" and event
timeout.
When something is said to be a request error for
exception exception and event event run these
steps:
The user agent should cancel any network
activity for which the object is responsible. If there are any
tasks from the
object's XMLHttpRequest task source in one of
the task queues,
then remove them.
Set the the error flag.
Change the state to DONE. If the synchronous flag is set,
throw an
exception exception and terminate the overall set of
steps. -
Fire an event named readystatechange.
At this point it is clear that the
synchronous flag is unset.
-
If the upload complete flag is unset, follow these
substeps:
Set the upload complete flag.
Fire a progress event named event
on the XMLHttpRequestUpload object.
Fire a progress event named
loadend on the XMLHttpRequestUpload
object.
Fire a progress event named event.
Fire a progress event named loadend.
When it is said to
run these steps:
Change the state to HEADERS_RECEIVED. Fire an event named readystatechange.
When it is said to
switch to the LOADING state run these
steps:
Change the state to LOADING. Fire an event named readystatechange.
When it is said to
switch to the DONE state run these steps:
If the synchronous flag is set, update the
response entity body. Unset the synchronous flag.
Change the state to DONE. Fire an event named readystatechange. Fire a progress event named load. Fire a progress event named loadend.
When it is said to make progress notifications, while the
download is progressing, queue a task to
fire a progress event named progress
about every 50ms or for every byte received, whichever is least
frequent.
When it is said to make upload progress notifications run
these steps:
4.7.8 The abort() method
- client .
abort() - Cancels any network activity.
The
abort()
method must run these steps (unless otherwise noted). This algorithm can
be terminated by invoking the
open() method. When it is
terminated the user agent
must terminate the algorithm after finishing the step it is on.
The abort()
algorithm can only be terminated by invoking
open() from an event
handler.
Terminate the send() algorithm. The user agent should cancel any network
activity for which the object is responsible. If there are any
tasks from the
object's XMLHttpRequest task source in one of
the task queues,
then remove them.
Set the error flag.
Unset the synchronous flag.
-
If the state is UNSENT,
OPENED with the
send() flag being unset, or
DONE go to the next step.
Otherwise run these substeps:
Change the state to DONE. Unset the send() flag.
Fire an event named readystatechange. Fire a progress event named abort. Fire a progress event named loadend. -
If the upload complete flag is false run these
substeps:
Set the upload complete flag to true. Fire a progress event named abort
on the XMLHttpRequestUpload object. Fire a progress event named loadend
on the XMLHttpRequestUpload object.
-
Change the state to UNSENT.
No readystatechange event is dispatched.
4.8 Response
4.8.1 The status attribute
- client .
status Returns the HTTP status code.
The
status
attribute must return the result of running these
steps:
If the state is
UNSENT or
OPENED, return 0 and
terminate these steps.
If the error flag is set, return 0 and terminate
these steps. Return the HTTP status code.
4.8.2 The statusText attribute
- client .
statusText Returns the HTTP status text.
The
statusText
attribute must return the result of running these steps:
If the state is
UNSENT or
OPENED, return the empty
string and terminate these steps.
If the error flag is set, return the empty string and
terminate these steps.
Return the HTTP status text.
- client .
getResponseHeader(header) Returns the header field value from the response of which the
field name matches header, unless the field name is
Set-Cookie or Set-Cookie2.
The
method must run these steps:
If the state is
UNSENT or
OPENED, return null and
terminate these steps.
If the error flag is set, return null and terminate
these steps.
If any code point in header is higher than
U+00FF LATIN SMALL LETTER Y WITH DIAERESIS, return null and terminate
these steps. Let header be the result of
deflating
header. If header is a case-insensitive match for
Set-Cookie or Set-Cookie2, return null and
terminate these steps. If header is a case-insensitive match for multiple HTTP
response headers, return the
inflated
values of these headers as a single concatenated string separated from
each other by a U+002C COMMA U+0020 SPACE character pair and terminate
these steps. If header is a case-insensitive match for a single HTTP
response header, return the
inflated
value of that header and terminate these steps. Return null.
The Cross-Origin Resource Sharing specification filters
the headers that are exposed by
getResponseHeader()
for non same-origin
requests. [CORS]
For the following script:
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.open("GET", "unicorns-are-teh-awesome.txt", true);
client.send();
client.onreadystatechange = function() {
if(this.readyState == 2) {
print(client.getResponseHeader("Content-Type"));
}
}
The print() function will get to process something
like:
text/plain; charset=UTF-8
- client .
getAllResponseHeaders() Returns all headers from the response, with the exception of those
whose field name is Set-Cookie or
Set-Cookie2.
The
method must run these steps:
If the state is
UNSENT or
OPENED, return the empty
string and terminate these steps.
If the error flag is set, return the empty string and
terminate these steps.
Return all the HTTP headers, excluding headers that are a
case-insensitive match for Set-Cookie or
Set-Cookie2,
inflated,
as a single string, with each header line
separated by a U+000D CR U+000A LF pair, excluding the status line, and
with each header name and header value separated by a
U+003A COLON U+0020 SPACE pair.
The Cross-Origin Resource Sharing specification filters
the headers that are exposed by
getAllResponseHeaders()
for non same-origin
requests. [CORS]
For the following script:
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.open("GET", "narwhals-too.txt", true);
client.send();
client.onreadystatechange = function() {
if(this.readyState == 2) {
print(this.getAllResponseHeaders());
}
}
The print() function will get to process something
like:
Date: Sun, 24 Oct 2004 04:58:38 GMT
Server: Apache/1.3.31 (Unix)
Keep-Alive: timeout=15, max=99
Connection: Keep-Alive
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
4.8.5 Response entity body
The response MIME type is the
MIME type the Content-Type header contains excluding any
parameters, or null if the response header can not be parsed or was
omitted. The override MIME type is
initially null and can get a value if overrideMimeType() is
invoked. Final MIME type is the
override MIME type unless that is null in which case it is the response MIME type.
The response charset is the value of
the charset parameter of the Content-Type header
or null if there was no charset parameter or the header could
not be parsed or was omitted. The
override charset is initially null and
can get a value if overrideMimeType() is invoked.
Final charset is the
override charset unless
that is null in which case it is the response charset.
The response entity body is the
fragment of the entity body of the
response received so far
(LOADING) or the complete
entity body of the response
(DONE). If the response
does not have an entity body, the
response entity body is null.
The response entity body is updated as part
of the send() algorithm.
The
arraybuffer response entity body
is an ArrayBuffer representing
the response entity body. If the
arraybuffer response entity body has no value assigned to it
let it be the return value of the following algorithm:
If the response entity body is null, return an empty
ArrayBuffer object and terminate
these steps. Return an ArrayBuffer
object representing the response entity body.
The
blob response entity body is a
Blob representing the response entity body. If
the blob response entity body has no value assigned to it let
it be the return value of the following algorithm:
If the response entity body is null, return an empty
Blob object and terminate these steps. Return a Blob object
representing the response entity body.
The
document response entity body
is either a
document
representing the response entity body or null. If it is a
document, its
origin is the
XMLHttpRequest origin. If the
document response entity body has no value assigned to it let
it be the return value of the following algorithm:
If the response entity body is null, return null and
terminate these steps. If final MIME type is not null,
text/html, text/xml,
application/xml, or does not end in
+xml, return null and terminate these steps.
-
If responseType is
the empty string and final MIME type is
text/html, return null and terminate these steps.
This is restricted to
responseType being
"document" in order to prevent breaking legacy
content.
-
If final MIME type is text/html let,
document be a
document that
represents the response entity body parsed following the
rules set forth in the HTML specification for an HTML parser with
scripting disabled. [HTML]
-
Otherwise, let document be a
document
that represents the result of parsing the
response entity body following the rules set forth in the
XML specifications. If that fails (unsupported character encoding,
namespace well-formedness error, etc.), return null and terminate these
steps.
[XML] [XMLNS]
Scripts in the resulting document tree will not be
executed, resources referenced will not be loaded and no associated XSLT
will be applied.
Return document.
The JSON response entity body is an ECMAScript value
representing the response entity body. The
JSON response entity body is the return value of the following
algorithm:
Let JSON text be the
response entity body decoded using UTF-8. Remove one leading
U+FEFF BYTE ORDER MARK character, if present. Return the result of invoking the parse function
of the JSON object defined in ECMAScript, with
JSON text as its only argument, or null if that function
throws an exception. [ECMASCRIPT]
The text response entity body
is a string representing the response entity body. The
text response entity body is the return value of the
following algorithm:
If the response entity body is null, return the empty
string and terminate these steps.
Let charset be the final charset. Let mime be the final MIME type. -
If responseType is
the empty string, charset is null, and mime is
either null, text/xml, application/xml or ends
in +xml, use the rules set forth in the XML
specifications to determine the character encoding. Let
charset be the determined character encoding.
[XML] [XMLNS]
This is restricted to
responseType being
the empty string to keep the non-legacy
responseType value
"text" simple.
-
If charset is null then, for each of the rows in the
following table, starting with the first one and going down, if the first
bytes of bytes match the bytes given in the first column, then
let charset be the encoding given in the cell in the second
column of that row. If there is no match charset remains
null.
| Bytes in Hexadecimal
| Description
|
| FE FF
| UTF-16BE BOM
|
| FF FE
| UTF-16LE BOM
|
| EF BB BF
| UTF-8 BOM
|
If charset is null let charset be
UTF-8. Return the result of decoding the
response entity body using charset. Replace bytes
or sequences of bytes that are not valid according to the
charset with a single
U+FFFD REPLACEMENT CHARACTER character. Remove one leading
U+FEFF BYTE ORDER MARK character, if present.
Authors are strongly encouraged to always encode their
resources using UTF-8.
4.8.6 The overrideMimeType() method
- client .
overrideMimeType(mime) -
Sets the Content-Type header for the response to
mime.
Throws an "InvalidStateError"
exception if the state is
LOADING or
DONE.
Throws a "SyntaxError" exception if
mime is not a valid media type.
The
overrideMimeType(mime)
method must run these steps:
If the state is
LOADING or
DONE,
throw an
"InvalidStateError" exception and
terminate these steps.
If parsing mime analogously to the value of
the Content-Type headers fails,
throw a
"SyntaxError" exception and terminate
these steps.
If a MIME type is successfully parsed set
override MIME type to that MIME type, excluding any parameters.
If a charset parameter is successfully parsed set
override charset to its value.
4.8.7 The responseType attribute
- client .
responseType [ = value ] -
Returns the response type.
Can be set to change the response type. Values are:
the empty string (default),
"arraybuffer",
"blob",
"document",
"json", and
"text".
When set: throws an
"InvalidStateError" exception if the
state is LOADING or
DONE.
When set: throws an
"InvalidAccessError" exception if the
synchronous flag is set and there is an associated
XMLHttpRequest document.
The
responseType
attribute must return its value. Initially its value must be the empty
string.
Setting the
responseType
attribute must run these steps:
If the state is
LOADING or
DONE,
throw an
"InvalidStateError" exception and
terminate these steps.
If there is an associated
XMLHttpRequest document and the
synchronous flag is set,
throw an
"InvalidAccessError" exception and
terminate these steps.
Set the
responseType
attribute's value to the given value.
4.8.8 The response attribute
- client .
response Returns the response entity body.
The
response
attribute must return the result of running these
steps:
- If
responseType
is the empty string or "text" -
If the state is not
LOADING or
DONE, return the empty
string and terminate these steps. If the error flag is set, return the empty string
and terminate these steps. Return the text response entity body.
- Otherwise
-
If the state is not
DONE, return null and
terminate these steps. If the error flag is set, return null and terminate
these steps. -
- If
responseType is
"arraybuffer" Return the
arraybuffer response entity body. - If
responseType is
"blob" Return the
blob response entity body. - If
responseType is
"document" Return the
document response entity body. - If
responseType is
"json" Return the
JSON response entity body.
4.8.9 The responseText attribute
- client .
responseText -
Returns the text response entity body.
Throws an "InvalidStateError"
exception if
responseType is not
the empty string or "text".
The
responseText
attribute must return the result of running these
steps:
If
responseType is not
the empty string or "text",
throw an
"InvalidStateError" exception and
terminate these steps.
If the state is not
LOADING or
DONE, return the empty
string and terminate these steps. If the error flag is set, return the empty string and
terminate these steps. Return the text response entity body.
4.8.10 The responseXML attribute
- client .
responseXML -
Returns the document response entity body.
Throws an "InvalidStateError"
exception if
responseType is not
the empty string or "document".
The
responseXML
attribute must return the result of running these steps:
If
responseType is not
the empty string or "document",
throw an
"InvalidStateError" exception and
terminate these steps. If the state is not
DONE, return null and
terminate these steps.
If the error flag is set, return null and terminate
these steps.
Return the document response entity body.
The
responseXML attribute
has XML in its name for historical reasons. It also returns HTML resources
as documents.
4.9 Events summary
This section is non-normative.
The following events are dispatched on XMLHttpRequest
and/or XMLHttpRequestUpload objects:
| Event name |
Interface |
Dispatched when… |
readystatechange |
Event |
The readyState
attribute changes at some seemingly arbitrary times for historical
reasons. |
loadstart |
ProgressEvent |
When the request starts. |
progress |
ProgressEvent |
While sending and loading data. |
abort |
ProgressEvent |
When the request has been aborted. For instance, by invoking the
abort() method. |
error |
ProgressEvent |
When the request has failed. |
load |
ProgressEvent |
When the request has successfully completed. |
timeout |
ProgressEvent |
When the author specified timeout has passed before the request
could complete. |
loadend |
ProgressEvent |
When the request has completed (either in success or failure). |
The FormData object represents an ordered collection of
entries. Each entry has a name, a value, a type, and optionally a
filename (if type is "file").
[Constructor,
Constructor(HTMLFormElement form)]
interface FormData {
void append(DOMString name, Blob value, optional DOMString filename);
void append(DOMString name, DOMString value);
};
- fd = new
FormData() Returns a new FormData object.
The FormData() constructor
must return a new FormData object.
The
FormData(form)
constructor must return a new FormData object with as entries
the result of
constructing the form data set for
form.
5.2 The append() method
- fd .
append(name, value [, filename]) Appends a new name/value-pair to the FormData
object, optionally with a filename.
The
append(name, value, filename)
method must create a new entry with the following parameters set and
append it to the end of the collection the FormData object
represents:
- Set its name to name.
- Set its value to value.
- Set its type to "text" if value is a string and "file" if
it is a
Blob.
- If its type is "file" set its filename to "
blob".
- If its type is "file" and value is a
File whose
name attribute
is not the empty string, set entry's filename to the attribute's value.
- If the filename parameter is not omitted set entry's
filename to filename.
References
Normative references
- [COOKIES]
- HTTP State Management Mechanism, Adam Barth. IETF.
- [CORS]
- Cross-Origin Resource Sharing, Anne van Kesteren. W3C.
- [DOM]
- DOM4, Anne van Kesteren, Aryeh Gregor and Ms2ger. W3C.
- [ECMASCRIPT]
- ECMAScript Language Specification. ECMA.
- [FILEAPI]
- File API, Arun Ranganathan and Jonas Sicking. W3C.
- [HTML]
- HTML, Ian Hickson. WHATWG.
- [HTTP]
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol -- HTTP/1.1, Roy Fielding, James Gettys, Jeffrey Mogul et al.. IETF.
- [HTTPAUTH]
- HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentication, J. Franks, Phillip Hallam-Baker, J. Hostetler et al.. IETF.
- [HTTPVERBSEC]
- Multiple vendors' web servers enable HTTP TRACE method by default. US-CERT.
- Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) vulnerable to cross-site scripting via HTTP TRACK method. US-CERT.
- HTTP proxy default configurations allow arbitrary TCP connections. US-CERT.
- [PROGRESSEVENTS]
- Progress Events, Anne van Kesteren. W3C.
- [RFC2119]
- Key words for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement Levels, Scott Bradner. IETF.
- [TYPEDARRAY]
- Typed Array, David Herman and Kenneth Russell. Khronos.
- [WEBIDL]
- Web IDL, Cameron McCormack. W3C.
- [XML]
- Extensible Markup Language, Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C. M. Sperberg-McQueen et al.. W3C.
- [XMLNS]
- Namespaces in XML, Tim Bray, Dave Hollander, Andrew Layman et al.. W3C.
Acknowledgments
The editor would like to thank
Addison Phillips,
Ahmed Kamel,
Alex Hopmann,
Alex Vincent,
Alexey Proskuryakov,
Asbjørn Ulsberg,
Boris Zbarsky,
Björn Höhrmann,
Cameron McCormack,
Chris Marrin,
Christophe Jolif,
Charles McCathieNevile,
Dan Winship,
David Andersson,
David Flanagan,
David Håsäther,
David Levin,
Dean Jackson,
Denis Sureau,
Doug Schepers,
Douglas Livingstone,
Elliotte Harold,
Eric Lawrence,
Eric Uhrhane,
Erik Dahlström,
Geoffrey Sneddon,
Gideon Cohn,
Gorm Haug Eriksen,
Håkon Wium Lie,
Hallvord R. M. Steen,
Henri Sivonen,
Huub Schaeks,
Ian Davis,
Ian Hickson,
Ivan Herman,
Jarred Nicholls,
Jeff Walden,
Jens Lindström,
Jim Deegan,
Jim Ley,
Joe Farro,
Jonas Sicking,
Julian Reschke,
呂康豪 (Kang-Hao Lu),
Karl Dubost,
Lachlan Hunt,
Maciej Stachowiak,
Magnus Kristiansen,
Marc Hadley,
Marcos Caceres,
Mark Baker,
Mark Birbeck,
Mark Nottingham,
Mark S. Miller,
Martin Hassman,
Mohamed Zergaoui,
Ms2ger,
Odin Hørthe Omdal,
Olli Pettay,
Pawel Glowacki,
Peter Michaux,
Philip Taylor,
Robin Berjon,
Rune Halvorsen,
Ruud Steltenpool,
Sergiu Dumitriu,
Sigbjørn Finne,
Simon Pieters,
Stewart Brodie,
Sunava Dutta,
Thomas Roessler,
Tom Magliery,
Yehuda Katz, and
Zhenbin Xu
for their contributions to this specification.
Special thanks to the Microsoft employees who first implemented the
XMLHttpRequest interface, which was first widely
deployed by the Windows Internet Explorer browser.
Special thanks also to the WHATWG for drafting an initial version of
this specification in their Web Applications 1.0 document (now renamed to
HTML). [HTML]
Thanks also to all those who have helped to improve this specification
by sending suggestions and corrections. (Please, keep bugging us with your
issues!)
Language/JAVASCRIPT 2013. 4. 29. 18:07
http://www.w3.org/TR/2012/NOTE-XMLHttpRequest1-20120117/#event-handler-attributes
Abstract
The XMLHttpRequest specification defines an API that provides scripted
client functionality for transferring data between a client and a server.
Status of this Document
Beware.
This specification was last published as a Candidate Recommendation,
but it is no longer in active maintenance, contains known errors,
and the Web Applications Working Group does not intend to maintain it further.
See XMLHttpRequest for the Working Group's latest specification.
This section describes the status of this document at the time of
its publication. Other documents may supersede this document. A list of
current W3C publications and the latest revision of this technical report
can be found in the W3C technical reports
index at http://www.w3.org/TR/.
This is the 17 January 2012 Working Group Note of
XMLHttpRequest. Please send comments to public-webapps@w3.org
(archived)
with [XHR-NOTE] at the start of the subject line.
Publication as a W3C Working Group Note does not imply endorsement
by the W3C Membership. This is a draft document and may be updated,
replaced or obsoleted by other documents at any time. It is inappropriate
to cite this document as other than work in progress.
This document is produced by the Web Applications (WebApps)
Working Group. The WebApps Working Group is part of the Rich Web Clients Activity
in the W3C Interaction
Domain.
This document was produced by a group operating under the 5 February
2004 W3C Patent Policy. W3C maintains a public list of any patent disclosures made in
connection with the deliverables of the group; that page also includes
instructions for disclosing a patent. An individual who has actual
knowledge of a patent which the individual believes contains Essential
Claim(s) must disclose the information in accordance with section
6 of the W3C Patent Policy.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
This section is non-normative.
The XMLHttpRequest object
implements an interface exposed by a scripting engine that allows scripts
to perform HTTP client functionality, such as submitting form data or
loading data from a server. It is the ECMAScript HTTP API.
The name of the object is XMLHttpRequest for compatibility
with the Web, though each component of this name is potentially
misleading. First, the object supports any text based format, including
XML. Second, it can be used to make requests over both HTTP and HTTPS
(some implementations support protocols in addition to HTTP and HTTPS, but
that functionality is not covered by this specification). Finally, it
supports "requests" in a broad sense of the term as it pertains to HTTP;
namely all activity involved with HTTP requests or responses for the
defined HTTP methods.
Some simple code to do something with data from an XML document fetched
over the network:
function test(data) {
// taking care of data
}
function handler() {
if(this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
// so far so good
if(this.responseXML != null && this.responseXML.getElementById('test').firstChild.data)
// success!
test(this.responseXML.getElementById('test').firstChild.data);
else
test(null);
} else if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status != 200) {
// fetched the wrong page or network error...
test(null);
}
}
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.onreadystatechange = handler;
client.open("GET", "unicorn.xml");
client.send();
If you just want to log a message to the server:
function log(message) {
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.open("POST", "/log");
client.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=UTF-8");
client.send(message);
}
Or if you want to check the status of a document on the server:
function fetchStatus(address) {
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.onreadystatechange = function() {
// in case of network errors this might not give reliable results
if(this.readyState == 4)
returnStatus(this.status);
}
client.open("HEAD", address);
client.send();
}
Everything in this specification is normative except for diagrams,
examples, notes and sections marked non-normative.
The key words must, must not, should, should not, and may in this document are to be interpreted as described in
RFC 2119. [RFC2119]
This specification defines the following classes of products:
- Conforming user agent
-
A user agent must behave as described in this
specification in order to be considered conformant.
If the user agent is not a conforming XML user agent the
XML response entity body must (always) be
null.
User agents may implement algorithms given in this
specification in any way desired, so long as the end result is
indistinguishable from the result that would be obtained by the
specification's algorithms.
This specification uses both the terms "conforming user
agent(s)" and "user agent(s)" to refer to this product class.
- Conforming XML user agent
-
An XML user agent must be a conforming user agent and must be a conforming XML processor that reports violations
of namespace well-formedness. [XML]
2.1. Dependencies
This specification relies on several underlying specifications.
- DOM
-
A conforming user agent must support at least
the subset of the functionality defined in DOM Events and DOM Core that
this specification relies upon, such as various exceptions and
EventTarget. [DOM2Events] [DOM3Core]
- HTML5
-
A conforming user agent must support at least the subset of the functionality
defined in HTML5 that this specification relies upon, such as the basics
of the Window object and serializing a
Document object. [HTML5]
The Window Object
1.0 draft is not referenced normatively as it appears to be no
longer maintained and HTML5 defines the Window object in
more detail. This specification already depends on HTML5 for other
reasons so there is not much additional overhead because of this.
- HTTP
-
A conforming user agent must support some
version of the HTTP protocol. Requirements regarding HTTP are made
throughout the specification. [RFC2616]
- Web IDL
-
A conforming user agent must also be a conforming implementation of the IDL
fragments in this specification, as described in the Web IDL
specification. [WebIDL]
2.2. Terminology
Convert a DOMString to a sequence of Unicode
characters is defined by the Web IDL specification. [WebIDL]
The term user credentials for the
purposes of this specification means cookies, HTTP authentication, and
client-side SSL certificates. Specifically it does not refer to proxy
authentication or the Origin header. [COOKIES]
The terms and algorithms <fragment>, <scheme>, cookie-free Document
object, document base URL, document's character encoding, event handler attributes, event handler event type, fetch, fully active, Function, innerHTML, origin, preferred MIME
name, resolve a URL, same origin, storage
mutex, task, task
source, task queues, URL, URL character
encoding, queue a task, and valid MIME type are defined by the HTML5
specification. [HTML5]
The term entity body is used as described in
RFC 2616. Method token is used as described in
section 5.1.1 of RFC 2616. field-name and field-value are used as described in
section 4.2 of RFC 2616. [RFC2616]
To deflate a DOMString
into a byte sequence means to create a sequence of bytes such that
the nth byte of the sequence is equal to the low-order
byte of the nth code point in the original DOMString.
To inflate a byte
sequence into a DOMString means to create a DOMString such that the
nth code point has 0x00 as the high-order byte and the
nth byte of the byte sequence as the low-order byte.
userinfo is used as described in
section 3.2.1 of RFC 3986. [RFC3986]
To dispatch a
readystatechange event means that an event with the
name readystatechange, which
does not bubble and is not cancelable, and which uses the
Event interface, is to be dispatched at the XMLHttpRequest object.
2.3. Extensibility
User agents, Working Groups, and other interested parties are
strongly encouraged to discuss extensions on a relevant public
forum, preferably public-webapps@w3.org. If this is
for some reason not possible prefix the extension in some way and start
the prefix with an uppercase letter. E.g. if company Foo wants to add a
private method bar() it could be named FooBar()
to prevent clashes with a potential future standardized
bar().
3. The XMLHttpRequest Interface
The XMLHttpRequest object can
be used by scripts to programmatically connect to their originating server
via HTTP.
[NoInterfaceObject]
interface XMLHttpRequestEventTarget : EventTarget {
// for future use
};
[Constructor]
interface XMLHttpRequest : XMLHttpRequestEventTarget {
// event handler attributes
attribute Function onreadystatechange;
// states
const unsigned short UNSENT = 0;
const unsigned short OPENED = 1;
const unsigned short HEADERS_RECEIVED = 2;
const unsigned short LOADING = 3;
const unsigned short DONE = 4;
readonly attribute unsigned short readyState;
// request
void open(DOMString method, DOMString url);
void open(DOMString method, DOMString url, boolean async);
void open(DOMString method, DOMString url, boolean async, DOMString? user);
void open(DOMString method, DOMString url, boolean async, DOMString? user, DOMString? password);
void setRequestHeader(DOMString header, DOMString value);
void send();
void send(Document data);
void send([AllowAny] DOMString? data);
void abort();
// response
readonly attribute unsigned short status;
readonly attribute DOMString statusText;
DOMString getResponseHeader(DOMString header);
DOMString getAllResponseHeaders();
readonly attribute DOMString responseText;
readonly attribute Document responseXML;
};
3.1. Origin and Base
URL
Each XMLHttpRequest object
has an associated XMLHttpRequest origin and an
XMLHttpRequest base
URL.
This specification defines their values when the global object is
represented by the Window object. When the XMLHttpRequest object is used in
other contexts their values will have to be defined as appropriate for
that context. That is considered to be out of scope for this
specification.
In environments where the global object is represented by the
Window object the XMLHttpRequest object has an
associated XMLHttpRequest
Document which is the Document object
associated with the Window object for which the XMLHttpRequest interface object
was created.
The XMLHttpRequest
Document is used to determine the XMLHttpRequest origin and
XMLHttpRequest base
URL at a later stage.
3.2. Task Sources
The task source used by this specification is
the XMLHttpRequest task
source.
3.3. Constructors
- client = new
XMLHttpRequest()
- Returns a new
XMLHttpRequest object.
When the XMLHttpRequest() constructor
is invoked, the user agent must return a new XMLHttpRequest object.
3.4. Event Handler
Attributes
The following is the event handler attribute (and its corresponding event handler event type) that must be supported as DOM attribute by the XMLHttpRequest object:
3.5. States
- client .
readyState
-
Returns the current state.
The XMLHttpRequest object can
be in several states. The readyState
attribute must return the current state, which must be one of the following values:
UNSENT (numeric value
0)
-
The object has been constructed.
OPENED (numeric value
1)
-
The open() method has been
successfully invoked. During this state request headers can be set using
setRequestHeader()
and the request can be made using the send() method.
-
(numeric value 2)
-
All redirects (if any) have been followed and all HTTP headers of the
final response have been received. Several response members of the
object are now available.
LOADING (numeric
value 3)
-
The response entity body is being
received.
DONE (numeric value 4)
-
The data transfer has been completed or something went wrong during
the transfer (e.g. infinite redirects).
The OPENED state has an associated send() flag that indicates whether the send() method has been invoked.
It can be either true or false and has an initial value of false.
The DONE state has an associated error flag that indicates some type of network error
or abortion. It can be either true or false and has an initial value of
false.
3.6. Request
The XMLHttpRequest object
holds the following request metadata variables:
- The asynchronous flag
- True when fetching is done
asychronously. False when fetching is done synchronously.
- The request method
- The method used in the request.
- The request URL
- The URL used in the request.
- The request username
- The username used in the request or null if there is no username.
- The request password
- The password used in the request or null if there is no password.
- The
- A list consisting of HTTP header name/value pairs to be used in the
request.
- The request entity body
- The entity body used in the request.
3.6.1. The open() method
- client .
open(method, url, async, user,
password)
-
Sets the request method, request URL, asynchronous flag, request username, and request password.
Throws a SYNTAX_ERR exception if one of the following is
true:
- method is not a valid HTTP method.
- url cannot be resolved.
- url contains the
"user:password"
format in the userinfo production.
Throws a SECURITY_ERR
exception if method is a case-insensitive match for
CONNECT, TRACE or TRACK.
Throws a SECURITY_ERR
exception if the origin of url
does not match the XMLHttpRequest origin.
Throws a NOT_SUPPORTED_ERR exception if the <scheme> of url is not supported.
When the open(method, url, async, user,
password) method is invoked, the user
agent must run these steps (unless otherwise indicated):
-
If the XMLHttpRequest
object has an associated XMLHttpRequest
Document run these substeps:
-
If the XMLHttpRequest
Document is not fully
active raise an INVALID_STATE_ERR exception and
terminate the overall set of steps.
-
Let XMLHttpRequest
base URL be the document base URL
of the XMLHttpRequest
Document.
-
Let XMLHttpRequest
origin be the origin of the XMLHttpRequest
Document.
-
If any code point in method is higher than U+00FF LATIN
SMALL LETTER Y WITH DIAERESIS or after deflating method it does not
match the Method token production raise a
SYNTAX_ERR exception and terminate these steps. Otherwise
let method be the result of deflating method.
-
If method is a case-insensitive match for
CONNECT, DELETE, GET,
HEAD, OPTIONS, POST,
PUT, TRACE, or TRACK subtract
0x20 from each byte in the range 0x61 (ASCII a) to 0x7A (ASCII z).
If it does not match any of the above, it is passed through
literally, including in the final request.
-
If method is a case-sensitive match for
CONNECT, TRACE, or TRACK raise a
SECURITY_ERR exception and
terminate these steps.
Allowing these methods poses a security risk. [HTTPVERBSEC]
-
Let url be a URL.
-
Let URL character encoding of
url be UTF-8.
-
Resolve url relative to the XMLHttpRequest base
URL. If the algorithm returns an error raise a
SYNTAX_ERR exception and terminate these steps.
-
Drop <fragment> from url.
-
If url contains an unsupported <scheme> raise a
NOT_SUPPORTED_ERR and terminate these steps.
-
If the "user:password" format in the userinfo production is not supported
for the relevant scheme and url contains this format
raise a SYNTAX_ERR and terminate these steps.
-
If url contains the "user:password"
format let temp user be the user part and temp
password be the password part.
-
If url just contains the "user"
format let temp user be the user part.
-
If the origin of url is not
same origin with the XMLHttpRequest origin
raise a SECURITY_ERR exception
and terminate these steps.
-
Let async be the value of the async argument or
true if it was omitted.
-
If the user argument was not omitted follow these sub
steps:
-
If user is null let temp user be null.
-
Otherwise let temp user be user.
These steps override anything that may have been set by the
url argument.
-
If the password argument was not omitted follow these sub
steps:
-
If password is null let temp password be null.
-
Otherwise let temp password be password.
These steps override anything that may have been set by the
url argument.
-
Abort the
send() algorithm.
-
The user agent should cancel any network activity
for which the object is responsible.
-
If there are any tasks from the
object's XMLHttpRequest task
source in one of the task queues, then
remove those tasks.
-
Set variables associated with the object as follows:
-
Switch the the state to OPENED.
-
Dispatch a
readystatechange event.
- client .
setRequestHeader(header, value)
-
Appends an header to the list of author request headers or if the
header is already in the author
request headers its value appended to.
Throws an INVALID_STATE_ERR exception if the state is not
OPENED or if the send() flag is true.
Throws a SYNTAX_ERR exception if header is not a valid HTTP header field name or if value is not a valid HTTP header field value.
As indicated in the algorithm below certain headers cannot be
set and are left up to the user agent. In addition there are certain other
headers the user agent will take control of if they are not set by the
author as indicated at the end of the send() method section.
When the method is
invoked, the user agent must run these steps:
-
If the state is not OPENED raise an
INVALID_STATE_ERR exception and terminate these steps.
-
If the send() flag is true raise
an INVALID_STATE_ERR exception and terminate these steps.
-
If any code point in header is higher than U+00FF LATIN
SMALL LETTER Y WITH DIAERESIS or after deflating header it does not
match the field-name production raise a
SYNTAX_ERR exception and terminate these steps. Otherwise
let header be the result of deflating header.
-
If any code point in value is higher than U+00FF LATIN
SMALL LETTER Y WITH DIAERESIS or after deflating value it does not
match the field-value production raise a
SYNTAX_ERR exception and terminate these steps. Otherwise
let value be the result of deflating value.
The empty string is legal and represents the empty header
value.
-
Terminate these steps if header is a case-insensitive match
for one of the following headers:
Accept-Charset
Accept-Encoding
Connection
Content-Length
Cookie
Cookie2
Content-Transfer-Encoding
Date
Expect
Host
Keep-Alive
Referer
TE
Trailer
Transfer-Encoding
Upgrade
User-Agent
Via
… or if the start of header is a case-insensitive
match for Proxy- or Sec- (including when
header is just Proxy- or Sec-).
The above headers are controlled by the user agent to let
it control those aspects of transport. This guarantees data integrity to
some extent. Header names starting with Sec- are not
allowed to be set to allow new headers to be minted that are guaranteed
not to come from XMLHttpRequest.
-
If header is not in the author request headers list append
header with its associated value to the list and
terminate these steps.
-
If header is in the author request headers list either
use multiple headers, combine the values or use a combination of those
(section 4.2, RFC 2616). [RFC2616]
See also the send() method regarding user
agent header handling for caching, authentication, proxies, and cookies.
// The following script:
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.open('GET', 'demo.cgi');
client.setRequestHeader('X-Test', 'one');
client.setRequestHeader('X-Test', 'two');
client.send();
// ...would result in the following header being sent:
...
X-Test: one, two
...
3.6.3. The send() method
- client .
send(data)
-
Initiates the request. The optional argument provides the request entity body. The argument is
ignored if request method is
GET or HEAD.
Throws an INVALID_STATE_ERR exception if the state is not
OPENED or if the send() flag is true.
When the send(data)
method is invoked, the user agent must run the following
steps (unless otherwise noted). This algorithm gets aborted when the open() or abort() method is invoked. When
the send()
algorithm is aborted the user agent must terminate
the algorithm after finishing the step it is on.
The send() algorithm can only be
aborted when the asynchronous flag is
true and only after the method call has returned.
-
If the state is not OPENED raise an
INVALID_STATE_ERR exception and terminate these steps.
-
If the send() flag is true raise
an INVALID_STATE_ERR exception and terminate these steps.
-
If the request method is a
case-sensitive match for GET or HEAD act as if
data is null.
If the data argument has been omitted or is null, do not
include a request entity body and go
to the next step.
Otherwise, let encoding be null, mime type be
null, and then follow these rules:
- If data is a
Document
-
Let encoding be the preferred MIME name of the character encoding of data. If
encoding is UTF-16 change it to UTF-8.
Let mime type be "application/xml;charset="
followed by encoding.
Let the request entity body be
the result of getting the innerHTML attribute on data
converted to Unicode and encoded as
encoding. Re-raise any exception this raises.
In particular, if the document cannot be serialized an
INVALID_STATE_ERR exception is raised.
Subsequent changes to the Document have no
effect on what is submitted.
- If data is a
DOMString
-
Let encoding be UTF-8.
Let mime type be "text/plain;charset=UTF-8".
Let the request entity body be
data converted to
Unicode and encoded as UTF-8.
If a Content-Type header is set using setRequestHeader()
whose value is a valid MIME type and has
a charset parameter whose value is not a case-insensitive
match for encoding, and encoding
is not null, set all the charset parameters of the
Content-Type header to encoding.
If no Content-Type header has been set using setRequestHeader()
and mime type is not null set a
Content-Type request header with as value mime type.
-
If the asynchronous flag is false
release the storage mutex.
-
Set the error flag to false.
-
If the asynchronous flag is true run
these substeps:
-
Set the send() flag to true.
-
Dispatch a
readystatechange event.
The state does not change. The event is dispatched for
historical reasons.
-
Return the send() method call, but
continue running the steps in this algorithm.
-
Fetch the request URL
from origin XMLHttpRequest origin,
with the synchronous flag set if the asynchronous flag is false, using HTTP
method request method, user request username (if non-null) and password
request password (if non-null), taking
into account the request entity body,
list of author request headers and
the rules listed at the end of this section.
- If the asynchronous flag is false
-
While making the request also follow the same-origin request event
rules.
The send() method call will now
be returned by virtue of this algorithm ending.
- If the asynchronous flag is true
-
Make progress notifications.
Make upload progress notifications.
While processing the request, as data becomes available and when the
user interferes with the request, queue tasks to update the response entity body and follow the
same-origin request event
rules.
If the user agent allows the end user to configure a proxy it should modify the request appropriately; i.e., connect to
the proxy host instead of the origin server, modify the
Request-Line and send Proxy-Authorization
headers as specified.
If the user agent supports HTTP Authentication and Authorization is not in the list of author request headers, it should consider requests originating from the XMLHttpRequest object to be part
of the protection space that includes the accessed URIs and send Authorization headers and handle 401
Unauthorized requests appropriately.
If authentication fails, Authorization is not in the list of author request headers, request username is null, and request password is null, user agents should prompt the end user for their username and password.
If authentication fails, Authorization is not in the list of author request headers, request username is non-null, and request password is non-null, user agents must not prompt the end user for their username and
password. [RFC2617]
End users are not prompted if username/password are provided
through the open() API so that authors can
implement their own user interface.
If the user agent supports HTTP State Management it should persist, discard and send cookies (as received in the
Set-Cookie and Set-Cookie2 response headers, and
sent in the Cookie header) as applicable. [COOKIES]
If the user agent implements a HTTP cache it should
respect Cache-Control request headers set by the setRequestHeader()
(e.g., Cache-Control: no-cache bypasses the cache). It must not send Cache-Control or
Pragma request headers automatically unless the end user
explicitly requests such behavior (e.g. by reloading the page).
For 304 Not Modified responses that are a result of a user
agent generated conditional request the user agent must
act as if the server gave a 200 OK response with the
appropriate content. The user agent must allow setRequestHeader() to
override automatic cache validation by setting request headers (e.g.
If-None-Match or If-Modified-Since), in which
case 304 Not Modified responses must be
passed through. [RFC2616]
If the user agent implements server-driven content-negotiation it should set Accept-Encoding and
Accept-Charset headers as appropriate. For
Accept and Accept-Language the user agent must follow these constraints:
Responses must have the content-encodings
automatically decoded. [RFC2616]
Besides the author request headers
user agents should not include additional request
headers other than those mentioned above or other than those authors are
not allowed to set using setRequestHeader().
This ensures that authors have a reasonably predictable API.
3.6.4.
Infrastructure for the send() method
The same-origin request event
rules are as follows:
- If the response has an HTTP status code of 301, 302, 303, or 307
-
If the origin of the URL
conveyed by the Location header is same origin with the XMLHttpRequest origin and
the redirect does not violate infinite loop precautions, transparently
follow the redirect while observing the same-origin request event
rules.
Otherwise, this is a network error.
HTTP places requirements on the user agent regarding the
preservation of the request method and request entity body during redirects,
and also requires end users to be notified of certain kinds of automatic
redirections.
- If the end user cancels the request
-
This is an abort error.
- If there is a network error
-
In case of DNS errors, TLS negotiation failure, or other type of
network errors, this is a network error. Do
not request any kind of end user interaction.
This does not include HTTP responses that indicate some
type of error, such as HTTP status code 410.
- Once all HTTP headers have been received and the asynchronous flag is true (and this is not
an HTTP redirect)
-
Switch to the HEADERS_RECEIVED
state.
- Once the first byte (or more) of the response entity body has been received
and the asynchronous flag is true
- If there is no response entity
body and the asynchronous flag is
true
-
Switch to the LOADING state.
- Once the whole response entity
body has been received
- If there is no response entity
body and the asynchronous flag is
false or the state is LOADING
-
Switch to the DONE state.
When something is said to be a network error
run the request error steps for exception NETWORK_ERR.
When something is said to be an abort error
run the request error steps for exception ABORT_ERR.
When something is said to be a request error
for exception exception run these steps:
-
The user agent should cancel any network activity
for which the object is responsible.
-
If there are any tasks from the
object's XMLHttpRequest task
source in one of the task queues, then
remove those tasks.
-
Set the response entity body to
null.
-
Empty the list of author request
headers.
-
Set the the error flag to true.
-
Switch the state to DONE.
-
If the asynchronous flag is false
raise an exception exception and terminate the overall set of
steps.
-
Dispatch a
readystatechange event.
At this point it is clear that the asynchronous flag is true.
-
Terminate the overall algorithm.
A future version of this specification will dispatch an error/abort event here as well.
(Depending on the type of error.)
When it is said to run these steps:
-
Switch the state to HEADERS_RECEIVED.
-
Dispatch a
readystatechange event.
When it is said to switch to the LOADING
state run these steps:
-
Switch the state to LOADING.
-
Dispatch a
readystatechange event.
When it is said to switch to the DONE state
run these steps:
-
If the asynchronous flag is false
update the response entity body.
-
Switch the state to DONE.
-
Dispatch a
readystatechange event.
3.6.5. The abort() method
- client .
abort()
- Cancels any network activity.
When the abort() method is
invoked, the user agent must run these steps (unless
otherwise noted):
-
Abort the
send() algorithm.
-
The user agent should cancel any network activity
for which the object is responsible.
-
If there are any tasks from the
object's XMLHttpRequest task
source in one of the task queues, then
remove those tasks.
-
Set the response entity body to
null.
-
Empty the list of author request
headers.
-
Set the error flag to true.
-
If the state is UNSENT, OPENED with the send() flag being false, or DONE
go to the next step.
Otherwise run these substeps:
-
Switch the state to DONE.
-
Set the send() flag to false.
-
Dispatch a
readystatechange event.
A future version of this specification will dispatch an
abort event here.
-
Switch the state to UNSENT.
No readystatechange event is
dispatched.
3.7. Response
3.7.1. The status attribute
- client .
status
-
Returns the HTTP status code.
The status attribute must return the result of running these steps:
-
If the state is UNSENT or OPENED return 0 and terminate these
steps.
-
If the error flag is true return 0 and
terminate these steps.
-
Return the HTTP status code.
3.7.2. The statusText attribute
- client .
statusText
-
Returns the HTTP status text.
The statusText
attribute must return the result of running these steps:
-
If the state is UNSENT or OPENED return the empty string and
terminate these steps.
-
If the error flag is true return the empty
string and terminate these steps.
-
Return the HTTP status text.
- client .
getResponseHeader(header)
-
Returns the header field value from the response of which the field
name matches header, unless the field name is
Set-Cookie or Set-Cookie2.
When the is invoked, the user agent must run these steps:
-
If the state is UNSENT or OPENED return null and terminate
these steps.
-
If the error flag is true return null and
terminate these steps.
-
If any code point in header is higher than U+00FF LATIN
SMALL LETTER Y WITH DIAERESIS return null and terminate these steps.
-
Let header be the result of deflating header.
-
If header is a case-insensitive match for
Set-Cookie or Set-Cookie2 return null and
terminate these steps.
-
If header is a case-insensitive match for multiple HTTP
response headers, return the inflated values of these headers as a single
concatenated string separated from each other by a U+002C COMMA U+0020
SPACE character pair and terminate these steps.
-
If header is a case-insensitive match for a single HTTP
response header, return the inflated value of that header and terminate these
steps.
-
Return null.
For the following script:
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.open("GET", "unicorns-are-teh-awesome.txt", true);
client.send();
client.onreadystatechange = function() {
if(this.readyState == 2) {
print(client.getResponseHeader("Content-Type"));
}
}
The print() function will get to process something like:
text/plain; charset=UTF-8
- client .
getAllResponseHeaders()
-
Returns all headers from the response, with the exception of those
whose field name is Set-Cookie or Set-Cookie2.
When the
method is invoked, the user agent must run the following
steps:
-
If the state is UNSENT or OPENED return the empty string and
terminate these steps.
-
If the error flag is true return the empty
string and terminate these steps.
-
Return all the HTTP headers, excluding headers that are a
case-insensitive match for Set-Cookie or
Set-Cookie2, inflated, as a single string, with each header line
separated by a U+000D CR U+000A LF pair, excluding the status line, and
with each header name and header value separated by a U+003A COLON
U+0020 SPACE pair.
For the following script:
var client = new XMLHttpRequest();
client.open("GET", "narwhals-too.txt", true);
client.send();
client.onreadystatechange = function() {
if(this.readyState == 2) {
print(this.getAllResponseHeaders());
}
}
The print() function will get to process something like:
Date: Sun, 24 Oct 2004 04:58:38 GMT
Server: Apache/1.3.31 (Unix)
Keep-Alive: timeout=15, max=99
Connection: Keep-Alive
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
3.7.5. Response
Entity Body
The response MIME type is the MIME type
the Content-Type header contains without any parameters or
null if the header could not be parsed properly or was omitted. The override MIME type is always null. Final MIME type is the override MIME type unless
that is null in which case it is the response MIME type.
The response charset is the value of the
charset parameter of the Content-Type header or
null if there was no charset parameter or if the header could
not be parsed properly or was omitted. The override charset is always null. Final charset is the override charset unless that
is null in which case it is the response charset.
Override MIME type and override charset are introduced here solely
to make editing several levels of XMLHttpRequest simultaneously somewhat
easier. Apologies for any confusion they might cause.
The response entity body is the
fragment of the entity body of the response
received so far (LOADING) or the complete entity body
of the response (DONE). If the response does not have an
entity body the response entity body is null.
The response entity body
is updated as part of the send() algorithm.
The text response entity body is
a DOMString representing the response entity body. The text response
entity body is the return value of the following algorithm:
-
If the response entity body is null return the empty string and
terminate these steps.
-
Let charset be the final
charset.
-
Let mime be the final MIME
type.
-
If charset is null and mime is null,
text/xml, application/xml or ends in +xml use the rules set forth in the XML specifications
to determine the character encoding. Let charset be the
determined character encoding.
-
If charset is null and mime is
text/html follow the rules set forth in the HTML
specification to determine the character encoding. Let
charset be the determined character encoding. [HTML5]
-
If charset is null then, for each of the rows in the
following table, starting with the first one and going down, if the
first bytes of bytes match the bytes given in the first
column, then let charset be the encoding given in the cell in
the second column of that row. If there is no match charset
remains null.
| Bytes in Hexadecimal
| Description
|
| FE FF
| UTF-16BE BOM
|
| FF FE
| UTF-16LE BOM
|
| EF BB BF
| UTF-8 BOM
|
-
If charset is null let charset be UTF-8.
-
Return the result of decoding the response entity body using
charset. Replace bytes or sequences of bytes that are not
valid accordng to the charset with a single U+FFFD
REPLACEMENT CHARACTER character.
Authors are strongly encouraged to encode their resources
using UTF-8.
The document response entity
body is either a Document representing the response entity body or null. The
document response entity body is the return value of the following
algorithm:
-
If the response entity body is
null terminate these steps and return null.
-
If final MIME type is not null,
text/xml, application/xml, and does not end in
+xml terminate these steps and return null.
-
Let document be a cookie-free Document
object that represents the result of parsing the response entity
body into a document tree following the rules from the XML
specifications. If this fails (unsupported character encoding, namespace
well-formedness error et cetera) terminate these steps return null.
[XML]
Scripts in the resulting document tree will not be
executed, resources referenced will not be loaded and no associated XSLT
will be applied.
-
Return document.
3.7.6. The responseText attribute
- client .
responseText
-
Returns the text response entity
body.
The responseText
attribute must return the result of running these steps:
-
If the state is not LOADING or DONE
return the empty string and terminate these steps.
-
Return the text response entity
body.
3.7.7. The responseXML attribute
- client .
responseXML
-
Returns the document response
entity body.
The responseXML
attribute must return the result of running these steps:
-
If the state is not DONE return null and terminate these
steps.
-
Return the document response
entity body.
4. Exceptions
Several algorithms in this specification may result in an exception
being thrown. These exceptions are all part of the group
ExceptionCode and use the DOMException object,
which is defined in DOM Level 3 Core. In addition this specification
extends the ExceptionCode group with several new constants as
indicated below. [DOM3Core]
Thus, exceptions used by this specification and not defined
in this section are defined by DOM Level 3 Core.
const unsigned short SECURITY_ERR = 18;
const unsigned short NETWORK_ERR = 19;
const unsigned short ABORT_ERR = 20;
The SECURITY_ERR exception is
raised if an attempt is made to perform an operation or access some data
in a way that would be a security risk or a violation of the user agent's
security policy.
The NETWORK_ERR exception is
raised when a network error occurs in synchronous requests.
The ABORT_ERR exception is raised
when the user aborts a request in synchronous requests.
These exceptions will be folded into an update of DOM Level 3
Core in due course, as they are appropriate for other API specifications
as well.
References
Unless marked "Non-normative" these references are normative.
- [COOKIES]
- HTTP State
Management Mechanism (work in progress), A. Barth. IETF.
- [DOM2Events]
- Document
Object Model (DOM) Level 2 Events Specification, T. Pixley.
W3C.
- [DOM3Core]
- Document Object
Model (DOM) Level 3 Core Specification, A. Le Hors, P. Le
Hégaret, L. Wood, G. Nicol, J. Robie, M. Champion, S. Byrne. W3C.
- [ECMAScript]
- ECMAScript
Language Specification. ECMA.
- [HTML5]
- HTML5
(work in progress), I. Hickson. W3C.
- HTML5
(work in progress), I. Hickson. WHATWG.
- [HTTPVERBSEC]
- (Non-normative) Multiple vendors' web
servers enable HTTP TRACE method by default, US-CERT.
- (Non-normative) Microsoft Internet
Information Server (IIS) vulnerable to cross-site scripting via HTTP
TRACK method, US-CERT.
- (Non-normative) HTTP proxy default
configurations allow arbitrary TCP connections, US-CERT.
- [RFC2046]
- Multipurpose Internet Mail
Extensions (MIME) Part Two: Media Types, N. Freed, N.
Borenstein. IETF.
- [RFC2119]
- Key words for use in RFCs
to Indicate Requirement Levels, S. Bradner. IETF.
- [RFC2616]
- Hypertext Transfer
Protocol -- HTTP/1.1, R. Fielding, J. Gettys, J. Mogul, H.
Frystyk, L. Masinter, P. Leach, T. Berners-Lee. IETF.
- [RFC2617]
- HTTP Authentication: Basic
and Digest Access Authentication, P. Hallam-Baker, J.
Hostetler, S. Lawrence, P. Leach, A. Luotonen, L. Stewart. IETF.
- [RFC3986]
- Uniform Resource
Identifier (URI): Generic Syntax, T. Berners-Lee, R. Fielding,
L. Masinter. IETF.
- [RFC3987]
- Internationalized Resource
Identifiers (IRIs), M. Duerst, M. Suignard. IETF.
- [WebIDL]
- Web
IDL (work in progress), C. McCormack. W3C.
- [XML]
- Extensible Markup Language
(XML) 1.0, T. Bray, J. Paoli, C. Sperberg-McQueen, E. Maler,
F. Yergeau. W3C.
- Namespaces in
XML, T. Bray, D. Hollander, A. Layman, R. Tobin, H. S.
Thompson. W3C.
Acknowledgments
The editor would like to thank Addison Phillips, Ahmed Kamel, Alex
Hopmann, Alex Vincent, Alexey Proskuryakov, Asbjørn Ulsberg, Boris
Zbarsky, Björn Höhrmann, Cameron McCormack, Christophe Jolif,
Charles McCathieNevile, Dan Winship, David Andersson, David
Håsäther, David Levin, Dean Jackson, Denis Sureau, Doug
Schepers, Douglas Livingstone, Elliotte Harold, Eric Lawrence, Erik
Dahlström, Geoffrey Sneddon, Gideon Cohn, Gorm Haug Eriksen,
Håkon Wium Lie, Hallvord R. M. Steen, Huub Schaeks, Ian Davis, Ian
Hickson, Ivan Herman, Jeff Walden, Jens Lindström, Jim Deegan, Jim
Ley, Joe Farro, Jonas Sicking, Julian Reschke, Karl Dubost, Lachlan Hunt,
Maciej Stachowiak, Magnus Kristiansen, Marc Hadley, Marcos Caceres, Mark
Baker, Mark Birbeck, Mark Nottingham, Mark S. Miller, Martin Hassman,
Mohamed Zergaoui, Olli Pettay, Pawel Glowacki, Peter Michaux, Philip
Taylor, Robin Berjon, Rune Halvorsen, Ruud Steltenpool, Simon Pieters,
Stewart Brodie, Sunava Dutta, Thomas Roessler, Tom Magliery, and Zhenbin
Xu for their contributions to this specification.
Special thanks to the Microsoft employees who first implemented the
XMLHttpRequest interface, which was first widely
deployed by the Windows Internet Explorer browser.
Special thanks also to the WHATWG for drafting an initial version of
this specification in their Web Applications 1.0 document (now renamed to
HTML5). [HTML5]
Thanks also to all those who have helped to improve this specification
by sending suggestions and corrections. (Please, keep bugging us with your
issues!)
Language/JSP 2013. 4. 23. 18:12
Open source로 구해지는 java source code를 들여다 보면
하고 많은 문자셋들 중에 유독 '8859_1'을 많이 보게 된다.
'아니 저런 특정 문자셋을, 그것도 8비트밖에 지원하지 않는 문자셋을 코드에다 박아 버리면
쓰는 사람들은 어쩌란 거지?'
이런 생각이 들 때가 있을 것이다.
한때 나도 그랬었고..
그러나 정말 잘못 쓴 경우도 있겠지만, 많은 경우 '8859_1'의 사용은 나름 합리성을 띄고 있다.
이를 이해하려면 '8859_1'이 다른 문자셋들과 어떻게 다른가를 알아야 한다.
이전 글에서 언급했 듯이, '8859_1'은 1바이트에 해당하는 256개의 코드에 대해, 즉 0x00 ~ 0xff 까지의 모든 코드에 대해 대응되는 문자를 갖고 있다.
반면 8859_1보다 많은 문자를 거느리고 있는 'EUC-KR',
이것의 확장형인 'MS949' 나 심지어 모든 글자를 다 포함한다고 여겨도 될 만한 'UTF-8' 조차
가진 문자는 확실히 많지만 모든 바이트 열에 대해 대응되는 문자를 갖고 있는 것은 아니다.
이를 확인하기 위해 다음을 실행해 보자.
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 256; j++) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[] {(byte) i, (byte)j };
String str = new String(bytes, "MS949");
if (str.charAt(0) == 0xfffd) {
System.out.println("for byte sequence{0x" + hex(i) + ", 0x" + hex(j)
+ "} no character exists... getBytes()[0]=" + str.getBytes("MS949")[0]);
} else if (str.length() > 1) {
// 첫 바이트를 하나의 글자로 인식. i만 취하고 j 루프는 중지.
System.out.println("For character{" + hex(i) + "} char = "
+ str.charAt(0));
break;
} else {
System.out.println("for character{" + hex(i) + ", " + hex(j)
+ "} char = " + str);
}
}
}
}
/*
* byte 출력용.
*/
public static String hex(int i ){
String hex = Integer.toHexString(i);
return (hex.length() > 2) ? hex.substring(hex.length() - 2) : hex;
}
주루룩 많은 행을 출력하지만 보면 대응되지 않는 글자가 존재함을 알 수 있다.
대략 그림으로 나타내면 다음과 같다.
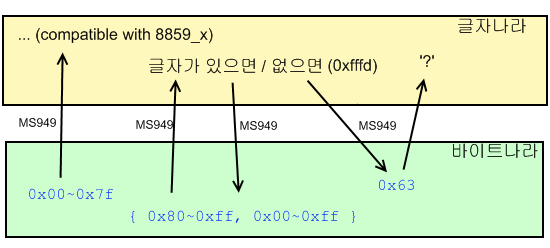 인식하는 바이트 값이 0x~0x7f 일 경우에는 8859_x 에서 사용되는 글자를 그대로 쓰며 이 때는 한 바이트가 하나의 글자와 매핑된다. 바이트 값이 0x81 이상일 경우에는 그 다음 바이트가 필요하며, 두 바이트를 가지고 하나의 글자를 구성한다. 그리고 이 때 '없는 글자'가 생긴다.
당장 {0x81, 0x00} ~ {0x81, 0x40} 에 해당하는 값에 대해 대응되는 글자가 없다.
없는 글자는 java char로 0xfffd (아마도 UTF-16BE로 {0xff 0xfd} 에 매핑되는 글자) 로 저장되었다가, 다시 MS949로 인코드하면 0x63 글자로 매핑된다. 이 글자가 물음표 '?' 이다
모르는 글자를 인코드 할 때 0x63 코드를 매핑하는 것은 Sun JDK에서의 대응 방식이다.
모르는 글자에 대한 대응에는 표준이 없는지 다른 vendor - 이를테면 IBM - 의 JDK에서는 좀 다르게 구현하는 것 같다.
(한편 바이트 값이 0x80이나 0xff 같을 때 이를 디코드하면 그 한 바이트가 '모르는 글자 0xfffd'로 매핑된다. 일반화할 수 있는 규칙은 아닌 것 같다..)
다음과 같이 인코드 - 디코드를 많이 거치게 되면 인코드 할 때도, 디코드 할 때도 매핑이 불가한 경우를 만나게 되어 글자들이 깨진다. 이 때의 깨진 글자들은 복구가 절대 안 된다.
그래서 저런 식으로 부주의하게 인코드-디코드를 해 버리면 원래 호환되는 0x00~0x7f 이외의 한글 같은 글자들은 여지없이 깨져 버리고.. 되돌릴 수도 없게 된다.
그러나 8859_x 는 모든 바이트 코드에 대한 글자들을 구비하고 있으므로, 이해가 안 되는 이상한 글자로 매핑할 망정 코드를 보존하면서 디코드가 가능하다.
그래서 디코드만 하고, 이를 다시 인코드 할 경우에는 글자 깨짐이 발생하지 않는다.
8859_1 뿐만 아니라 8859_2 도 "보관"할 때 가지는 문자가 틀리지만 역시 깨짐 없이 바이트를 보존할 수 있다.
물론 그렇게 "보관"한 문자나 인코드가 원활히 되지, 아무 문자열이나 인코드를 하려 한다면
'자기 문자셋에 존재하지 않는 문자를 인코드'하는 경우가 발생해 글자가 깨질 것이다.
이를테면 아래와 같은 경우 당연히 문자셋에 없는 글자를 인코드하려 하므로 글자가 깨진다.
이렇게 되면 '원래 문자열이 2글자였다' 정도 외엔 아무 정보도 남지 않게 된다. (JDK vendor에 따라서는 이마저도 알 수 없게 될 것이다)
-----------------------------
실제 네트워크를 오가는 데이터는 바이트열의 형태이지만
이를 프로그래밍 언어에서 다룰 때는 문자열로 간주하고 작업할 때가 많다.
그게 편하기 때문이기도 하고,
문자열로서 의미를 가지는 경우가 많기 때문이기도 할 것이다.
가장 많이 쓰이는 경우가 웹 어플리케이션에서의 파일 다운로드, 아마도 그 다음이 소켓통신 (헤더를 읽어들이거나 생성할 때) 같은 경우일 것이다.
<< 다운로드 시 설정>>
response.addHeader("Content-disposition", "attachment;filename=" + ... + "" );
이 때 인코딩/디코딩 작업이 필요한데, 디코드 시 바이트들을 깨뜨리지 않고 문자열로 얻고 싶다면 '8859_x'을 쓰는 것이 현명한 방책이라 하겠다.
물론 그 중에서도 많은 서버들이 위의 filename 을 ISO-Latin1(혹은 Latin1, 8859_1) 로 인코딩 해 보내기 때문에 같은 Latin 계열이라도 '8859_1' 즉 'Latin1'을 택하는 것이 좋다.
이는 표준이라고 하는데 문서 확인은 안 해 봤다. (어디 있는지 찾기 정말 힘들던데..)
출처 - http://blog.naver.com/anabaral?Redirect=Log&logNo=130043451093
Language/JSP 2013. 4. 23. 18:10
개요
웹프로그래밍을 하다보면 항상 한글인코딩과 관련된 문제에 봉착하게 된다.
그럴때면 보통 웹검색을 통해 대부분의 해결책을 찾고는 하였다. 하지만, 그 해결책이라는 것이 대부분 경험담에 불과하고, 우리가
맞닥뜨린 문제와는 미묘하게 다른부분이 있기도 하여 근본적인 해결방법이 되지 않을 경우도 있다. 우연찮게 해결을 하더라도, 시간에
쫒기다보니, 근본적인 원인을 해결하지 못하고 해결하기에 급급하여 다음에 또 비슷한문제를 겪는 악순환을 겪기도 한다.
실제로 톰캣에서 한글이 어떻게 인코딩/디코딩되는걸까? 본인 역시 늘 고민해오던 문제였는데, 마침 시간이 나게되어, JSP파일에서부터 클라이언트의 응답메시지와 요청메시지, 그리고 톰캣에서의 인코딩과정에 대해 간략하게 정리해보았다.
이 글은 톰캣 5.5.x, 와 6.0.x 에서 테스트 되었다.
JSP 인코딩과 HTML 인코딩
우리가 작성한 JSP 파일은 컨테이너(여기서는 톰캣)에 의해 JAVA 파일로 변경이 된다.
이때 첫번째 인코딩이 일어나게 되는데, 이 시점에서 확인하여야할것은 JSP 파일 인코딩과 JSP 문자 인코딩이다. JSP 파일 인코딩과 JSP 문자 인코딩이 다를 경우 여지없이 한글이 깨져 버린다.
JSP 파일 인코딩은 실제 해당 파일이 작성될때 사용된 캐릭터셋으로 Eclipse 같은 툴을 사용하면 확인할 수 있다. 
JSP 문자 인코딩은 컨테이너가 JSP파일을 JAVA로 변경하기위해 읽어들일때, 해당 JSP파일이 어떤 문자셋으로 이루어져 있는가를 컨테이너에게 알려주기 위해 JSP의 page 지시자에 선언되어 있는 캐릭터셋이다.
JSP 파일의 문자 인코딩 캐릭터셋은 JSP의 page 지시자의 속성중에 pageEncoding를 확인하면 된다. 디폴트 값은 ISO-8859-1 이지만, ContentType에서 인코딩을 정의 하지 않았을
경우에만 디폴트 값이 적용된다.
예를 들어 다음과 같은 내용의 JSP파일을 생성하였다고 가정하자. (파일 인코딩은 UTF-8이라고 가정한다)
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="EUC-KR"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>테스트</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<form action="/test2.jsp" method="post">
<input type="text" name="keyword" > <input type="submit">
</form> </div>
</body>
</html> |
다음은 위의 JSP 파일이 변경된 JAVA 파일의 일부이다.
(서블릿을 컨테이너에 배포한다음 TOMCAT_HOME/work/ 하위에서 찾을 수 있다)
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("<head>\r\n");
out.write("<meta http-equiv=\"Content-Type\" content=\"text/html; charset=UTF-8\">\r\n");
out.write("<title>�����/title>\r\n");
out.write("</head>\r\n");
out.write("<body>\r\n");
out.write("<div> \r\n");
out.write("\t<form action=\"/test2.jsp\" method=\"post\">\r\n");
out.write("\t\t<input type=\"hidden\" name=\"actions\" value=\"test2\" >\r\n
|
JSP의 <title>의 한글이 깨져 있음을 확인할 수 있다.
page 지시자에는 pageEncoding 뿐만 아니라 contentType 이라는 속성도 있는데, 이 속성은 MIME 타입과 해당 페이지에서 사용될 인코딩 문자셋을 설정한
다. 즉, 이 값에 따라 브라우져가 서버의 메시지를 어떤 문자셋으로 해석할지가 결정되며, 페이지에서 사용되는 문자들의 인코딩
문자셋이 결정된다. 대부분의 브라우져의 기능을 살펴보면 문자 인코딩을 변경하는 메뉴가 있는데, 여기에 기본으로 선택된 값이
contentType에 설정된 값이다. 
contentType 이 생략될 경우 pageEncoding 값을 따르며, pageEncoding 까지 생략되면 기본적으로 ISO-8859-1 문자셋을 따른다.
예를 들어 contentType의 값이 UTF-8 이라면 클라이언트의 브라우져는 서버의 응답을 UTF-8로 해석하여 HTML 파일을 화면에 뿌리게 된다. 그리고 페이지의 모든 문자들은 UTF-8의 문자셋을 기반으로 하게된다.
HTML의 meta 태그내의 content 속성은 단순히 메타 태그로써 페이지의 정보를 알려주는 기능외에 실제 인코딩에 관여하지 않는다는 것에 주의하도록 한다.
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=EUC-KR">
<title>test</title>
</head> |
서블릿과 톰캣 인코딩
톰
캣은 클라이언트에서 서버로의 요청메시지를 서블릿 스펙에 따라 기본적으로 ISO-8859-1 로 인코딩되어 처리되도록 되어 있다.
즉, 클라이언트에서의 문자열이(contentType) UTF-8 이든, EUC-KR 이든 ISO-8859-1로 인코딩 된다는
것이다.
(메시지의 인코딩은 앞에서 언급한바대로 웹페이지의 ContetType 값에 따른다)
즉, 다음의 코드가 실행되는 것과 같다.
//UTF-8 인코딩된 메시지
new String( "UTF-8".getByte("UTF-8"),"ISO-8859-1");
//EUC-KR 인코딩된 메시지
new String("EUC-KR".getByte("EUC-KR"),"ISO-8859-1");
|
어
라? 이상하지 않은가? 한글 처리를 위한 UTF-8이나 EUC-KR은 2바이트 문자인데, 1바이트 문자인 ISO-8859-1로
인코딩하면 문자열이 깨지지 않겠는가? 깨어지는 것처럼 보이지만 실제로는 문자열의 바이트값이 보존된다. 여기서 인코딩/디코딩의
개념과 ISO-8859-1 이라는 문자셋에 대한 이해가 필요하다.
우선 문자셋이라는 것은 글자와 바이트의 매핑관계를 정의하는 것으로 문자셋에 따라 이 매핑관계가 달라진다. 예를 들어 EUC-KR문자셋에서 "테스트" 라는 문자열은 "c5d7bdbac6ae" 바이트배열값으로 매핑된다. 이때 EUC-KR 문자셋은 2바이트 문자셋이므로 c57b값이 "테" 라는 문자열값에 매핑되며 7bdb와 c6ae는 각각 "스"와 "트"에 매핑이된다.
이렇게 문자열을 바이트 시퀀스로 변환하는 과정을 인코딩, 그 반대 과정을 디코딩이라고 한다. 이
론적으로 EUC-KR은 2바이트 문자로써 65535개의 문자를 매핑하는것이 가능하지만 실제로는 대부분의 바이트가 비어있다. 이는
UTF-8이나 KSC5601, MS949 등 마찬가지이다. 문자셋들은 동일한 바이트값에 대한 매핑문자가 서로 다르며, 문자
구성또한 달라 매핑이 불가능한 문자도 있다. 예를 들어 유니코드 "뷁" 문자를 EUC-KR 로 인코딩할경우 "뷁" 문자가
EUC-KR 문자셋에 정의되어 있지 않으므로, 자바는 이를 "?(0X3F)"로 변경해버린다. (이 또한 JVM 벤더에 따라 다르게
동작한다.) "?"로 매칭된 문자는 원래의 유니코드로 디코딩된다고 해도 원래의 "뷁" 문자를 표현하지 못하게된다. 이처럼
문자간의 인코딩/디코딩시에 데이터 손실이 일어나게되는데, ISO-8859-1 문자셋은 1바이트로 이루어져있지만, 유일하게
빈공간없이 모든 바이트값에 대해 문자를 매핑하고 있다. 따라서, ISO-8859-1 문자셋으로 인코딩되었다하더라도 원래 문자셋으로
디코딩만 하면 데이터의 손실없이 원래의 문자를 표현할수 있게된다.
ISO-8859-1 문자셋에 대해서는 다음을 참고하라 (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO/IEC_8859-1#ISO-8859-1)
다시 톰캣이야기로 돌아가서 위에서 언급하길 서블릿 스펙에 따라 톰캣은 모든 요청메시지를 ISO-8859-1로 인코딩한다고 하였다.
즉, EUC-KR 문자열의 바이트 값인 "c5d7bdbac6ae"를 톰캣이
받게되면 이 바이트 배열을 ISO-8859-1 문자셋으로 인코딩된것으로 간주하고 ISO-8859-1문자셋을 이용해 디코딩해버린다.
그렇게 되면 "c5d7bdbac6ae" 바이트배열은"Å×½ºÆ®" 이라는 문자열로 디코딩되는데, ISO-8859-1문자셋은 각
바이트에 매칭되는 문자값이 모두 존재하기때문에 의미없는 문자로 표현될지언정 매칭문자가 없어 "?"로 표현될 일이 없다. 즉,
문자열이 깨지지 않는다. 따라서, "Å×½ºÆ®" 문자열을 다시 EUC-KR 문자셋으로 인코딩하게되면 원래의 문자열로 돌아가게되는것이 보장된다.
byte[] bytes = "테스트".getBytes("EUC-KR");
String str = new String(bytes,"ISO-8859-1");
System.out.println(hex(bytes)); //hex() 는 바이트 배열값을 HEX코드로 출력하는 기능
System.out.println(str);
bytes = "Å×½ºÆ®".getBytes("ISO-8859-1");
str = new String(bytes,"EUC-KR");
System.out.println(hex(bytes));
System.out.println(str);
=============================================
c5d7bdbac6ae
Å×½ºÆ®
c5d7bdbac6ae
테스트
|
톰캣으로 전달된 ISO-8859-1 인코딩된 데이터는 톰캣 내부에서 사용자의 요청메시지를 처리하기위해 request 객체를
생성하는 과정에서 인코딩 과정을 거치게된다. 이때 적용되는 인코딩 문자셋은 기본적으로 null로써 시스템 프로퍼티인
file.encoding에 정의된 인코딩 문자셋(이하, 시스템 인코딩 문자셋)을 사용하도록 되어 있다. 클라이언트의 요청메시지의
원래 인코딩 문자셋과 시스템 인코딩 문자셋이 다르다면 원래의 문자셋으로 복원이 불가능해지므로 한글 인코딩이 깨어지게 된다. 따라서
한글 데이터를 보존하기 위해서는 new String("문자열".getByte("ISO-8859-1"), "EUC-KR") 같이 클라이언트에서 전송시에 사용된 문자셋으로 디코딩 과정을 먼저 실행한다음 원래대로 문자열을 복원하여야 한다. 번거로운 인코딩작업 대신에 클라이언트의 요청 메시지 전체에 대해 명시적으로 인코딩 문자셋을 지정해주는 방법이 있는데, 그 방법은 아래와 같다. (단 인코딩 문자셋은 request 객체가 생성되기전에 정의되어야 한다)
| request.setCharacterEncoding("문자셋이름") |
톰
캣은 클라이언트의 요청메시지에 대한 request 객체의 생성이 끝나면, 응답 메시지를 작성하기위해 response 객체를
생성하게 된다. 이때 response 객체의 생성시에 사용되는 인코딩 문자셋은 JSP 파일의 page 지시자의
contentType 속성에 정의된 인코딩 문자셋을 따르게 된다. 서버의 응답 메시지를 생성할때 사용되는 인코딩 문자셋과
브라우져에서 이를 해석하는 문자셋이 항상 contentType을 따르도록 되어있으므로 프로그래머는 이 단계에서는 인코딩에 대해
신경쓰지 않아도 된다. 하지만 문제는 request 객체와 response 객체 사이에서 일어난다. 대부분의 응답메시지는
요청메시지의 데이터를 포함하게 되는데, 요청메시지에 대해 디코딩을 완벽하게 수행했다하더라도, request 객체와 response
객체의 인코딩 문자셋이 다르다면 request 객체의 데이터가 response 객체에서 인코딩이 깨어지게 된다.
이렇게 생성된 서버의 응답메시지는 ISO-8850-1 인코딩되어 클라이언트의 브라우져에 전달된다. 전달된 응답 메시지는 클라이언트의 브라우져에서 contentType에 정의된 인코딩 문자셋을 이용하여 해석된 다음 출력되게 된다.
GET과 POST
앞
절에서 클라이언트 요청메시지에 전체에 대해 명시적으로 인코딩 문자셋을 지정하는 방법을 소개하였다. 하지만 이 경우 request
객체가 생성되기 이전에 인코딩 문자셋을 지정하여야 하므로 톰캣에서는 필터를 사용하여 인코딩 문자셋을 지정할 것을 권장하고 있다.
하지만 이 경우에도 약간의 문제가 있다. 클라이언트의 요청메시지는 GET과 POST 두 가지 방식으로 서버에 전달되는데, 필터에
의한 인코딩 문자셋을 지정하는 방법은 POST요청에 한해서만 유효하다는 점이다. GET 방식으로 전달 되는 파라메터는 URL에
포함되어 전달되는데, URL은 요청 메시지 내부의 파라메터는 지정된 인코딩 문자셋을 사용하지않고 기본적으로 ISO-8859-1
인코딩 문자셋에 따라 해석을 하기 때문이다. 따라서 URL에 대한 인코딩 문자셋을 명시적으로 지정해줄 필요가 있다. 이를 위해서는
톰캣의 tomcat_home/conf/server.xml 파일의 Connector 부분의 설정을 변경하여야 한다. ...
<Connector ... port="8080" URIEncoding="UTF-8" />
...
|
정리지금 까지의 이야기를 정리하자면 한글을 적절하게 처리하기 위해서는 우선, 요청 페이지의 contentType을 확인해야 하며, 사용자의 요청메시지가 GET인지, POST인지를 확인한다. 그런다음 각각의 요청메시지 타입에 따라 서버에서 메시지를 처리하는 인코딩 문자셋을 확인한 다음, 마지막으로 응답 페이지의 contentType을 확인하여 이 4가지 인코딩 문자셋이 일치하는가를 살펴보아야 한다.
이
상의 내용은 실제 톰캣을 소스레벨까지 내려가서 살펴본것이아니라, 다분히 개인적인 지식과 경험에 의해 쓰여진 것이므로 다소 사실과는
다를지도 모른다. 하지만, 여러가지 실험과 근거에 의해 작성되었으므로 신뢰할 만하다고 생각한다. 한글 처리로 곤란함을 격게된다면
위의 과정을 밟아가면서 어디에서 인코딩이 깨지는가를 확인해보면 빠르게 문제를 해결을 할 수 있으리라 생각한다. 부디 한글로 인해
고민하는 날이 없기를 바란다.
출처 - http://blog.naver.com/codechaser?Redirect=Log&logNo=80085455490
Language/JAVASCRIPT 2013. 2. 22. 17:48
http://www.java2s.com/Tutorial/JavaScript/CatalogJavaScript.htm
Language/CSS 2013. 2. 21. 14:12
| <!DOCTYPE html> | | <html lang="en" class="no-js"> | | <head> | | <title>HTML5 inputs and attribute support</title> | | <meta name="keywords" content="html5, input, forms, attributes, browser support" /> | | <link rel="stylesheet" href="/css/core.css" /> | | <script src="/scripts/modernizr-1.0.js"></script> | | <script src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1/jquery.min.js"></script> | | <script src="/scripts/attr_support-min.js"></script> | | </head> | | <body id="input-attr-support"> | | <header> | | <hgroup> | | <h1>HTML5 inputs and attribute support</h1> | | <h3 id="ua"></h3> | | </hgroup> | | </header> | | <p>A red input (followed by frowny faces) indicates the browser does not support the input type.</p> | | <table id="text-search-url-tel-table"> | | <thead> | | <tr> | | <th><code><input></code></th> | | <th>type</th> | | <th>autocomplete</th> | | <th>autofocus</th> | | <th>list</th> | | <th>maxlength</th> | | <th>pattern</th> | | <th>placeholder</th> | | <th>readonly</th> | | <th>required</th> | | <th>size</th> | | </tr> | | </thead> | | <tbody> | | <tr id="text-row"> | | <th><input id="text" type="text" /></th> | | <th><label for="text">text</label></th> | | <td id="t_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="t_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="t_list"></td> | | <td id="t_maxlength"></td> | | <td id="t_pattern"></td> | | <td id="t_placeholder"></td> | | <td id="t_readonly"></td> | | <td id="t_required"></td> | | <td id="t_size"></td> | | </tr> | | <tr id="search-row"> | | <th><input id="search" type="search" /></th> | | <th><label for="search">search</label></th> | | <td id="s_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="s_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="s_list"></td> | | <td id="s_maxlength"></td> | | <td id="s_pattern"></td> | | <td id="s_placeholder"></td> | | <td id="s_readonly"></td> | | <td id="s_required"></td> | | <td id="s_size"></td> | | </tr> | | <tr id="url-row"> | | <th><input id="url" type="url" /></th> | | <th><label for="url">url</label></th> | | <td id="u_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="u_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="u_list"></td> | | <td id="u_maxlength"></td> | | <td id="u_pattern"></td> | | <td id="u_placeholder"></td> | | <td id="u_readonly"></td> | | <td id="u_required"></td> | | <td id="u_size"></td> | | </tr> | | <tr id="tel-row"> | | <th><input id="tel" type="tel" /></th> | | <th><label for="tel">tel</label></th> | | <td id="te_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="te_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="te_list"></td> | | <td id="te_maxlength"></td> | | <td id="te_pattern"></td> | | <td id="te_placeholder"></td> | | <td id="te_readonly"></td> | | <td id="te_required"></td> | | <td id="te_size"></td> | | </tr> | | </tbody> | | </table> | | <table id="email-table"> | | <thead> | | <tr> | | <th><code><input></code></th> | | <th>type</th> | | <th>autocomplete</th> | | <th>autofocus</th> | | <th>list</th> | | <th>maxlength</th> | | <th>multiple</th> | | <th>pattern</th> | | <th>placeholder</th> | | <th>readonly</th> | | <th>required</th> | | <th>size</th> | | </tr> | | </thead> | | <tbody> | | <tr id="email-row"> | | <th><input id="email" type="email" /></th> | | <th><label for="email">email</label></th> | | <td id="e_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="e_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="e_list"></td> | | <td id="e_maxlength"></td> | | <td id="e_multiple"></td> | | <td id="e_pattern"></td> | | <td id="e_placeholder"></td> | | <td id="e_readonly"></td> | | <td id="e_required"></td> | | <td id="e_size"></td> | | </tr> | | </tbody> | | </table> | | <table id="password-table"> | | <thead> | | <tr> | | <th><code><input></code></th> | | <th>type</th> | | <th>autocomplete</th> | | <th>autofocus</th> | | <th>maxlength</th> | | <th>pattern</th> | | <th>placeholder</th> | | <th>readonly</th> | | <th>required</th> | | <th>size</th> | | </tr> | | </thead> | | <tbody> | | <tr id="password-row"> | | <th><input id="password" type="password" /></th> | | <th><label for="password">password</label></th> | | <td id="p_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="p_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="p_maxlength"></td> | | <td id="p_pattern"></td> | | <td id="p_placeholder"></td> | | <td id="p_readonly"></td> | | <td id="p_required"></td> | | <td id="p_size"></td> | | </tr> | | </tbody> | | </table> | | <table id="datetime-date-month-week-time-table"> | | <thead> | | <tr> | | <th><code><input></code></th> | | <th>type</th> | | <th>autocomplete</th> | | <th>autofocus</th> | | <th>list</th> | | <th>max</th> | | <th>min</th> | | <th>readonly</th> | | <th>required</th> | | <th>step</th> | | </tr> | | </thead> | | <tbody> | | <tr id="datetime-row"> | | <th><input id="datetime" type="datetime" /></th> | | <th><label for="datetime">datetime</label></th> | | <td id="dt_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="dt_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="dt_list"></td> | | <td id="dt_max"></td> | | <td id="dt_min"></td> | | <td id="dt_readonly"></td> | | <td id="dt_required"></td> | | <td id="dt_step"></td> | | </tr> | | <tr id="date-row"> | | <th><input id="date" type="date" /></th> | | <th><label for="date">date</label></th> | | <td id="d_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="d_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="d_list"></td> | | <td id="d_max"></td> | | <td id="d_min"></td> | | <td id="d_readonly"></td> | | <td id="d_required"></td> | | <td id="d_step"></td> | | </tr> | | <tr id="month-row"> | | <th><input id="month" type="month" /></th> | | <th><label for="month">month</label></th> | | <td id="m_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="m_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="m_list"></td> | | <td id="m_max"></td> | | <td id="m_min"></td> | | <td id="m_readonly"></td> | | <td id="m_required"></td> | | <td id="m_step"></td> | | </tr> | | <tr id="week-row"> | | <th><input id="week" type="week" /></th> | | <th><label for="week">week</label></th> | | <td id="w_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="w_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="w_list"></td> | | <td id="w_max"></td> | | <td id="w_min"></td> | | <td id="w_readonly"></td> | | <td id="w_required"></td> | | <td id="w_step"></td> | | </tr> | | <tr id="time-row"> | | <th><input id="time" type="time" /></th> | | <th><label for="time">time</label></th> | | <td id="ti_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="ti_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="ti_list"></td> | | <td id="ti_max"></td> | | <td id="ti_min"></td> | | <td id="ti_readonly"></td> | | <td id="ti_required"></td> | | <td id="ti_step"></td> | | </tr> | | </tbody> | | </table> | | <table id="datetimelocal-number-table"> | | <thead> | | <tr> | | <th><code><input></code></th> | | <th>type</th> | | <th>autocomplete</th> | | <th>autofocus</th> | | <th>list</th> | | <th>max</th> | | <th>min</th> | | <th>readonly</th> | | <th>required</th> | | <th>step</th> | | </tr> | | </thead> | | <tbody> | | <tr id="datetimelocal-row"> | | <th><input id="datetime-local" type="datetime-local" /></th> | | <th><label for="datetime-local">datetimelocal</label></th> | | <td id="dtl_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="dtl_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="dtl_list"></td> | | <td id="dtl_max"></td> | | <td id="dtl_min"></td> | | <td id="dtl_readonly"></td> | | <td id="dtl_required"></td> | | <td id="dtl_step"></td> | | </tr> | | <tr id="number-row"> | | <th><input id="number" type="number" /></th> | | <th><label for="number">number</label></th> | | <td id="n_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="n_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="n_list"></td> | | <td id="n_max"></td> | | <td id="n_min"></td> | | <td id="n_readonly"></td> | | <td id="n_required"></td> | | <td id="n_step"></td> | | </tr> | | </tbody> | | </table> | | <table id="range-table"> | | <thead> | | <tr> | | <th><code><input></code></th> | | <th>type</th> | | <th>autocomplete</th> | | <th>autofocus</th> | | <th>list</th> | | <th>max</th> | | <th>min</th> | | <th>step</th> | | </tr> | | </thead> | | <tbody> | | <tr id="range-row"> | | <th><input id="range" type="range" /></th> | | <th><label for="range">range</label></th> | | <td id="r_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="r_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="r_list"></td> | | <td id="r_max"></td> | | <td id="r_min"></td> | | <td id="r_step"></td> | | </tr> | | </tbody> | | </table> | | <table id="color-table"> | | <thead> | | <tr> | | <th><code><input></code></th> | | <th>type</th> | | <th>autocomplete</th> | | <th>autofocus</th> | | <th>list</th> | | </tr> | | </thead> | | <tbody> | | <tr id="color-row"> | | <th><input id="color" type="color" /></th> | | <th><label for="color">color</label></th> | | <td id="c_autocomplete"></td> | | <td id="c_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="c_list"></td> | | </tr> | | </tbody> | | </table> | | <table id="checkbox-radio-table"> | | <thead> | | <tr> | | <th><code><input></code></th> | | <th>type</th> | | <th>autofocus</th> | | <th>checked</th> | | <th>required</th> | | </tr> | | </thead> | | <tbody> | | <tr id="checkbox-row"> | | <th><input id="checkbox" type="checkbox" /></th> | | <th><label for="checkbox">checkbox</label></th> | | <td id="cb_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="cb_checked"></td> | | <td id="cb_required"></td> | | </tr> | | <tr id="radio-row"> | | <th><input id="radio" type="radio" /></th> | | <th><label for="radio">radio button</label></th> | | <td id="rb_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="rb_checked"></td> | | <td id="rb_required"></td> | | </tr> | | </tbody> | | </table> | | <table id="file-upload-table"> | | <thead> | | <tr> | | <th><code><input></code></th> | | <th>type</th> | | <th>accept</th> | | <th>autofocus</th> | | <th>multiple</th> | | <th>required</th> | | </tr> | | </thead> | | <tbody> | | <tr id="file-row"> | | <th><input id="file" type="file" /></th> | | <th><label for="file">file</label></th> | | <td id="f_accept"></td> | | <td id="f_autofocus"></td> | | <td id="f_multiple"></td> | | <td id="f_required"></td> | | </tr> | | </tbody> | | </table> | | <p>See also <a href="/code/html5-forms-ui-support.html">html5 forms UI support</a> & <a href="/code/html5-textarea-attribute-support.html">html5 textarea attributes support</a>.</p> | | <p><a href="http://www.whatwg.org/specs/web-apps/current-work/multipage/the-input-element.html#input-type-attr-summary">Reference</a> <a href="http://gist.github.com/208473">Core Tests</a></p> | | <p class="small">Copyright © 2009 Michael Taylor (<a href="http://www.twitter.com/miketaylr">@miketaylr</a>) and licensed under the <a href="/code/license.txt">MIT license.</a> Special thanks to <a href="http://paulirish.com">Paul Irish</a>.</p> | | <script type="text/javascript">var gaJsHost = (("https:" == document.location.protocol) ? "https://ssl." : "http://www.");document.write(unescape("%3Cscript src='" + gaJsHost + "google-analytics.com/ga.js' type='text/javascript'%3E%3C/script%3E"));</script> | | <script type="text/javascript">try {var pageTracker = _gat._getTracker("UA-1911699-3");pageTracker._trackPageview();} catch(err) {}</script> | | </body> | | </html>
출처 - http://miketaylr.com/code/input-type-attr.html |
Language/jQuery 2013. 2. 19. 10:56
jQuery에서 검색 메소드 입니다.
다양한 검색 메소드들이 있지만 이 세가지 (find, filter, children) 메소드를 헷갈릴때가 있습니다.
filter : 현재 검색된 객체(집합)에서 다시 한번 검색하는 메소드
find : 현재 검색된 객체(집합)의 자손들에서 검색 하는 메소드, 자식의 레벨은 상관없습니다.
children : 현재 검색된 객체(집합)의 직속 자식만 검색하는 메소드
filter는 검색된 결과 객체 집합에서 특정 집합으로 다시 한번 검색 할때 사용합니다.
find 검색된 결과 객체 집합의 하위레벨을 다 뒤져서(자손) 검색 할때 사용 합니다.
children 검색된 결과 객체 집하의 바로 자식들만 뒤져서(자식) 검색 할때 사용합니다.
출처 - http://ddoong2.com/413
|